2 phosphonobutane 1 2 4 tricarboxylic acid
Exploring the Potential of 2% Phosphonobutane-1,2,4-tricarboxylic Acid
Phosphonobutane-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid, often abbreviated as PBTC, is a compound that has garnered significant attention in various fields due to its unique chemical properties and diverse application potential. This article aims to explore the functionality of 2% PBTC in different settings and its implications for various industries.
Chemical Structure and Properties
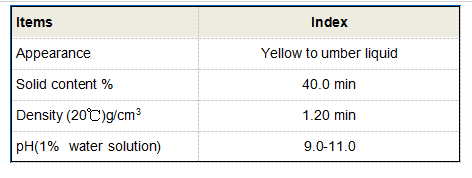
PBTC is a phosphonic acid derivative characterized by a butane backbone with three carboxylic acid groups attached. This structure endows PBTC with excellent chelating properties, making it effective in binding metal ions. The phosphonic acid group contributes not only to its acidic nature but also enhances its stability compared to other organic acids. When used in a 2% concentration, it demonstrates a balance between efficacy and safety for handling, which is crucial in industrial applications.
Applications in Industries
1. Water Treatment One of the most prominent applications of PBTC is in water treatment processes. Due to its ability to sequester calcium and magnesium ions, it effectively prevents the formation of scale in boilers and cooling systems. Scale buildup can lead to decreased efficiency and increased maintenance costs. By incorporating a 2% concentration of PBTC in water treatment formulations, industries can maintain optimal operating conditions while minimizing the risk of fouling.
2. Oil and Gas Industry The oil and gas sector significantly benefits from the use of PBTC as a scale inhibitor in drilling fluids and produced water. Scale formation can pose substantial challenges during extraction, often resulting in costly downtime. The application of PBTC in drilling operations helps maintain the flow of hydrocarbons while contributing to overall environmental safety, as its biodegradability makes it a more sustainable option compared to traditional inhibitors.
2 phosphonobutane 1 2 4 tricarboxylic acid
3. Detergency and Cleaning Products PBTC is also utilized in the formulation of detergents and cleaning products. Its chelating properties allow it to bind with metal ions found in hard water, thus enhancing the efficiency of surfactants. This means that products containing a 2% concentration of PBTC can achieve better cleaning results, making it a favored component in household and industrial cleaners.
4. Agriculture In agriculture, PBTC serves as a chelating agent for trace minerals, aiding in nutrient absorption by plants. By including PBTC in fertilizers, farmers can enhance the bioavailability of essential nutrients, potentially leading to improved crop yields. The 2% formulation strikes a functional balance, providing adequate nutrient delivery without causing toxicity to plants.
Safety and Environmental Considerations
While the benefits of PBTC are extensive, safety and environmental impact are paramount concerns in its application. A 2% concentration is typically seen as safe for many uses, but ongoing research is essential to continually assess its long-term effects on ecosystems and human health. Control measures should be in place to prevent excessive release into the environment, aligning with sustainability goals in various industries.
Conclusion
Phosphonobutane-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid presents a myriad of benefits across several fields, particularly in water treatment, oil and gas extraction, cleaning products, and agriculture. The 2% formulation of PBTC combines effectiveness with manageable safety, making it a versatile component in modern applications. Moving forward, as industries increasingly prioritize sustainability and efficiency, compounds like PBTC will continue to play a crucial role in meeting these demands while contributing to technological advancements. Ongoing research and development will be key to unlocking further potential of PBTC and ensuring its responsible use in the future.
-
lk-319-special-scale-and-corrosion-inhibitor-for-steel-plants-advanced-solutions-for-industrial-water-systemsNewsAug.22,2025
-
flocculant-water-treatment-essential-chemical-solutions-for-purification-processesNewsAug.22,2025
-
isothiazolinones-versatile-microbial-control-agents-for-industrial-and-consumer-applicationsNewsAug.22,2025
-
scale-inhibitor-key-solutions-for-water-system-scale-preventionNewsAug.22,2025
-
organophosphonates-versatile-scale-inhibitors-for-industrial-water-systemsNewsAug.22,2025
-
scale-and-corrosion-inhibitor-essential-chemical-solutions-for-water-system-maintenanceNewsAug.22,2025





