flocculant vs coagulant
Flocculant vs. Coagulant Understanding the Key Differences
In the realm of water treatment and purification, two pivotal substances play a critical role coagulants and flocculants. Although often used interchangeably, they serve distinct functions in the water treatment process, making it essential to understand their differences and applications.
Flocculant vs
. Coagulant Understanding the Key DifferencesOn the other hand, flocculants are substances that further enhance the aggregation of these already-formed flocs, making them larger and heavier. Flocculants typically consist of long-chain polymers that help bind smaller flocs together, facilitating their removal through sedimentation or filtration. They are often used after coagulation to improve the efficiency of the treatment process. Common flocculants include polyacrylamides and natural polymers such as starches and cellulose derivatives.
flocculant vs coagulant
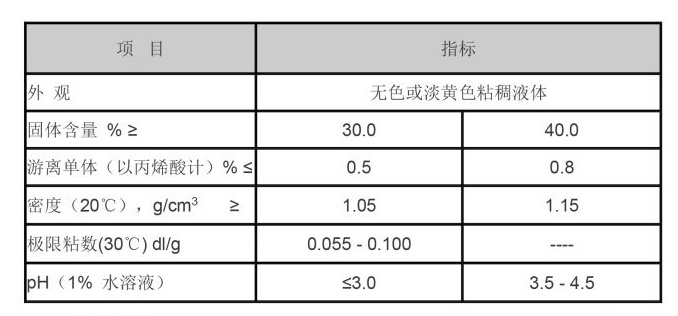
The choice between using a coagulant or a flocculant depends on the specific requirements of the water treatment process. Coagulants are usually effective in the early stage of treatment, while flocculants are employed later to enhance the settling of particles. This two-step process is essential in achieving optimal water quality, especially in municipal water treatment plants and industrial applications.
Moreover, the dosage of these substances is crucial. An inadequate amount of coagulant will result in insufficient floc formation, while excessive dosages can lead to incomplete settling and residual chemicals in the treated water. Similarly, overuse of flocculants can cause floc breakage, leading to poor separation.
In summary, while coagulants and flocculants both contribute to water purification, they perform different roles within the treatment process. Understanding their functions and proper applications is essential for achieving effective water treatment and ensuring safe, clean water for consumption and use.
-
Understanding Acrylic Homopolymers and Their ApplicationsNewsApr.01,2025
-
The Emerging Importance of Polyaspartic AcidNewsApr.01,2025
-
Poly Aluminum Chloride and Polyacrylamide: Key Players in Water TreatmentNewsApr.01,2025
-
Flocculants for Water TreatmentNewsApr.01,2025
-
Essential Solutions for Water Treatment and PurificationNewsApr.01,2025
-
Chemical Solutions for Advanced IndustriesNewsApr.01,2025





