Exploring the Chemical Properties and Applications of Polymaleic Anhydride in Modern Industries
Poly(maleic anhydride) Properties, Applications, and Future Prospects
Poly(maleic anhydride) (PMA) is a polymer derived from maleic anhydride, a compound that plays a pivotal role in the synthesis of various polymers and copolymers. This unique polymer possesses a range of physicochemical properties that make it suitable for diverse applications across several industries, from pharmaceuticals to environmental technology.
The structure of poly(maleic anhydride) is based on the repeated unit of maleic anhydride, a cyclic anhydride that, when polymerized, yields a linear polymer with an intricate network of polar functional groups. This architecture is responsible for its high reactivity and solubility in various solvents, making PMA an attractive candidate for further functionalization. The presence of the anhydride functional group also imparts excellent chemical stability and compatibility with other materials, leading to enhanced performance in composite formulations.
Poly(maleic anhydride) Properties, Applications, and Future Prospects
Additionally, PMA has found applications in the field of superabsorbent materials. Its excellent water retention capacity and biocompatibility make it ideal for use in products such as diapers, feminine hygiene products, and agricultural applications where moisture retention is critical. Moreover, the ability of PMA to form gels upon interaction with water enhances its versatility, further expanding its potential applications.
polymaleic anhydride
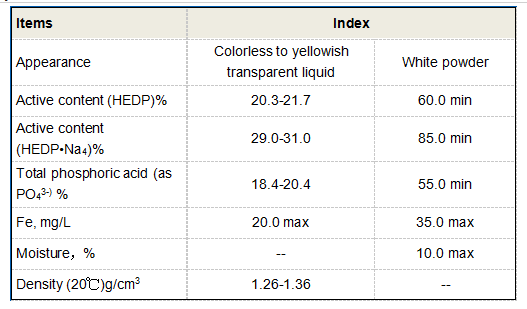
In the realm of environmental science, poly(maleic anhydride) has emerged as a valuable material for creating eco-friendly solutions. Its use in green chemistry is being explored due to its biodegradable nature and non-toxic degradation products. PMA-based polymers are being studied for their potential in water treatment processes, where they can be used to remove pollutants and heavy metals from wastewater. By optimizing the properties of PMA, researchers are investigating its role in contributing to sustainable practices in industrial processes.
Furthermore, the incorporation of PMA into composite materials is a growing area of interest. The polymer can act as a coupling agent, improving the mechanical properties and interfacial adhesion of various composites made from polymers, metals, and ceramics. This feature is particularly valuable in the automotive and aerospace industries, where lightweight and strong materials are crucial for enhancing performance and energy efficiency.
Looking ahead, the future of poly(maleic anhydride) appears promising. Ongoing research aims to unravel more of its potential through copolymerization with other monomers, which can tailor the properties for specific applications. Innovations in polymer chemistry could lead to the development of novel PMA-based materials that enhance performance while ensuring environmental sustainability.
In conclusion, poly(maleic anhydride) is a multifaceted polymer with unique properties that enable its application across various fields. From drug delivery systems to enhancing composite materials and contributing to eco-friendly initiatives, PMA represents a cornerstone of modern polymer science. As research continues to evolve, the potential of poly(maleic anhydride) will hopefully expand, leading to innovative solutions that address current challenges in technology and sustainability.
-
Pbtc Scale InhibitorPBTC: A Scale Protector for Industrial Water TreatmentNewsAug.05,2025
-
Organic Phosphonate: An Efficient Defender in the Field of Scale InhibitionNewsAug.05,2025
-
Hydrolyzed Polymaleic Anhydride: Green Pioneer in Scale Inhibition FieldNewsAug.05,2025
-
PAPEMP Polyamino Polyether Methylene Phosphonic Acid For SaleNewsAug.05,2025
-
Flocculant Water Treatment: A Pioneer in Purification in the Field of Water TreatmentNewsAug.05,2025
-
Benzyl Isothiazolinone: An Efficient and Broad-Spectrum Antibacterial Protective GuardNewsAug.05,2025





