Factors Influencing Scale Formation and Effectiveness of Corrosion Inhibitors in Industrial Applications
Understanding Scale and Corrosion Inhibitors Importance and Applications
Scale and corrosion are two significant challenges faced by various industries, from power plants to water treatment facilities. The buildup of scale, primarily composed of mineral deposits, can reduce efficiency and increase fuel consumption in thermal systems. Similarly, corrosion can lead to severe damage to equipment, resulting in costly repairs and safety hazards. To mitigate these issues, the use of scale and corrosion inhibitors has become essential in maintaining the integrity and efficiency of industrial systems.
What is Scale and How Does it Form?
Scale typically forms when dissolved minerals in water, such as calcium and magnesium, precipitate out of solution due to changes in temperature or pressure. This precipitation often occurs in heat exchangers, boilers, and pipelines, leading to the development of hard deposits that can obstruct flow pathways and reduce heat transfer efficiency. In severe cases, scale formation can lead to complete blockages, requiring extensive cleaning procedures or even equipment replacement.
The Nature of Corrosion
Corrosion, on the other hand, is an electrochemical process that leads to the deterioration of metals when they are exposed to environmental factors like moisture, oxygen, and certain chemicals. The result is the gradual loss of material from the metal surface, which can compromise the structural integrity of machinery and pipelines. Different types of corrosion, such as pitting, galvanic, and uniform corrosion, can occur depending on the environmental conditions and the materials involved.
The Role of Inhibitors
scale and corrosion inhibitor
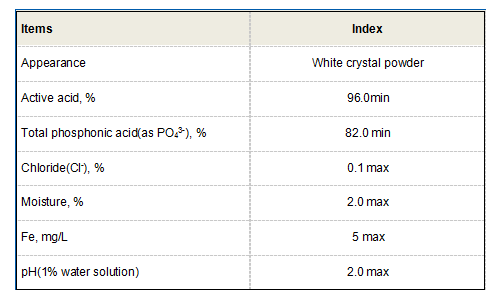
Scale and corrosion inhibitors are chemical substances specifically designed to prevent or reduce the formation of scale and the deterioration caused by corrosion. They work through various mechanisms, such as altering the properties of water to inhibit scale formation or creating protective films on metal surfaces to prevent corrosive attacks.
1. Types of Scale Inhibitors Common scale inhibitors include phosphate-based, polymer-based, and crystalline inhibitors. Phosphate-based inhibitors stabilize dissolved minerals, keeping them in solution and preventing precipitation. Polymer-based inhibitors interfere with the crystallization process, allowing for better control of scale formation. Crystalline inhibitors form protective coatings that trap scale and prevent its adherence to surfaces.
2. Types of Corrosion Inhibitors Corrosion inhibitors can be classified into anodic inhibitors, cathodic inhibitors, and mixed inhibitors. Anodic inhibitors, such as chromates, reduce the oxidation process, while cathodic inhibitors, like zinc salts, decrease the reduction process. Mixed inhibitors provide dual protection, addressing both anodic and cathodic reactions, effectively slowing down the corrosion rate.
Choosing the Right Inhibitor
The selection of an appropriate scale and corrosion inhibitor depends on several factors, including the type of equipment, the chemical composition of the water used, the operating conditions, and environmental regulations. Conducting a thorough assessment of these factors will help determine the most effective and economical inhibitor to use.
Conclusion
The implementation of scale and corrosion inhibitors is critical for the efficient operation of industrial systems. By preventing scale buildup and corrosion, these chemicals not only prolong equipment life but also optimize performance and reduce maintenance costs. As industries continue to seek sustainable and efficient solutions, the development and application of advanced inhibitors play a pivotal role in ensuring the reliability and safety of technological systems. Understanding their mechanisms and applications will empower industries to achieve better operational outcomes and environmental compliance, ultimately contributing to their long-term success.
-
Pbtc Scale InhibitorPBTC: A Scale Protector for Industrial Water TreatmentNewsAug.05,2025
-
Organic Phosphonate: An Efficient Defender in the Field of Scale InhibitionNewsAug.05,2025
-
Hydrolyzed Polymaleic Anhydride: Green Pioneer in Scale Inhibition FieldNewsAug.05,2025
-
PAPEMP Polyamino Polyether Methylene Phosphonic Acid For SaleNewsAug.05,2025
-
Flocculant Water Treatment: A Pioneer in Purification in the Field of Water TreatmentNewsAug.05,2025
-
Benzyl Isothiazolinone: An Efficient and Broad-Spectrum Antibacterial Protective GuardNewsAug.05,2025





