Preparation and Properties of Poly Aluminum Chloride Solution for Water Treatment Applications
Understanding Polyaluminum Chloride Solution Properties, Applications, and Benefits
Polyaluminum chloride (PAC) solutions have gained significant attention in various industrial and environmental applications due to their effective properties as a coagulant. This water-soluble compound, primarily used in water treatment processes, plays a crucial role in improving water quality by facilitating the removal of suspended solids, colloids, and other impurities.
Chemical Composition and Properties
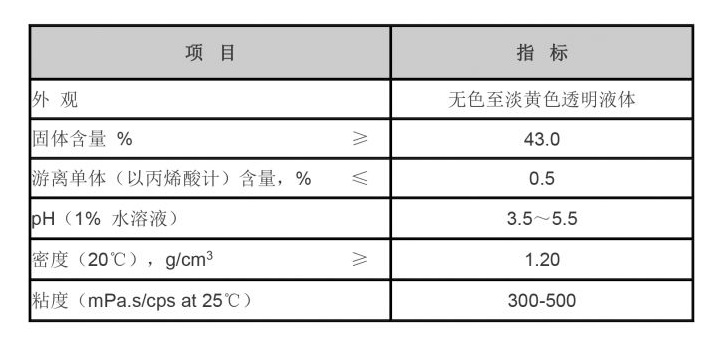
Polyaluminum chloride is composed of aluminum chloride and aluminum hydroxide. The formula can vary, but it typically represents a mixture of aluminum species in solution, characterized by a high positive charge that enhances its coagulation capabilities. The pH range for PAC solutions often falls between 4 and 6, making them less aggressive than other aluminum-based coagulants like aluminum sulfate. This property reduces the risk of corrosion in treatment plants and improves safety for operators.
One of the primary advantages of PAC is its versatility. It can function effectively at various pH levels, making it suitable for both acidic and alkaline water sources. Additionally, PAC has a lower dosage requirement compared to traditional coagulants, which translates into reduced chemical costs and minimized environmental impact.
Applications in Water Treatment
In water treatment facilities, PAC is predominantly employed for the clarification of drinking water, wastewater treatment, and sludge dewatering. The coagulant works by neutralizing the negative charges on suspended particles, allowing them to aggregate into larger flocs that can be easily removed through sedimentation or filtration processes.
polyaluminum chloride solution
For municipal water treatment, PAC has proven to reduce turbidity and improve the overall clarity of water. Its effectiveness in removing color and taste impurities makes it particularly beneficial in treating surface water sourced from lakes and rivers. Furthermore, in wastewater management, PAC enhances the removal of organic compounds and heavy metals, contributing to compliance with environmental regulations.
Benefits Over Traditional Coagulants
The use of PAC solutions offers several key benefits over traditional coagulants like aluminum sulfate. Firstly, PAC typically requires a significantly lower dosage for achieving optimal results. This efficiency not only lowers operational costs but also reduces the generation of sludge—a byproduct of the coagulation process. Consequently, treatment plants can save on disposal costs for sludge management, leading to both economic and environmental advantages.
Secondly, PAC is less sensitive to changes in water chemistry, including fluctuations in pH and temperature. This characteristic enables operators to maintain consistent treatment outcomes even under varying conditions, ultimately leading to improved system reliability.
Lastly, PAC has been observed to have a lower environmental impact. Its enhanced coagulation ability reduces the need for additional chemicals, which can contribute to chemical pollution in treated water. Moreover, the less voluminous sludge produced minimizes the ecological footprint of water treatment processes.
Conclusion
Polyaluminum chloride solutions have emerged as a vital component in modern water treatment technologies. With their superior coagulant properties, cost-effectiveness, and environmental benefits, PAC solutions provide an attractive alternative to traditional methods. As water quality standards become increasingly stringent worldwide, the demand for effective and efficient water treatment solutions like PAC is likely to grow, positioning it as a cornerstone for sustainable water management practices.
-
Understanding Polycarboxylic Acids: Properties, Applications, and Future PotentialNewsJul.28,2025
-
Scale Inhibitor Explained: How to Protect Your System from Limescale and Hard Water DamageNewsJul.28,2025
-
Scale and Corrosion Inhibitors: Essential Chemicals for Industrial Water System ProtectionNewsJul.28,2025
-
Polyaspartic Acid: A Biodegradable Polymer for Sustainable ChemistryNewsJul.28,2025
-
Isothiazolinones: A Versatile Antimicrobial Class with Industrial Power and Regulatory ChallengesNewsJul.28,2025
-
A Deep Dive into 2-Phosphonobutane-1,2,4-Tricarboxylic Acid (PBTC)NewsJul.28,2025





