scale and corrosion inhibitor
Understanding Scale and Corrosion Inhibitors Essential Tools for Industrial Water Systems
Scale and corrosion are two significant challenges faced by various industries that rely on water systems for their operations. From power generation to oil and gas processing, maintaining the efficiency and longevity of equipment is paramount. To combat these destructive processes, scale and corrosion inhibitors play a crucial role in protecting systems from the detrimental effects of mineral deposits and corrosion.
Understanding Scale and Corrosion
Scale refers to the accumulation of mineral deposits, primarily calcium carbonate, calcium sulfate, and other inorganic substances that crystallize out of water. This can occur in pipes, heat exchangers, boilers, and cooling towers, leading to reduced flow rates, increased energy consumption, and ultimately equipment failure. Scale formation is often driven by high temperatures, evaporation, and changes in pressure, all of which can promote the precipitation of minerals.
Corrosion, on the other hand, is the gradual destruction of materials (usually metals) due to chemical reactions with their environment, often involving oxygen and moisture. This process can lead to significant structural damage, leaks, and failures. The presence of dissolved gases, aggressive ions, and certain pH levels can accelerate corrosion, making it a persistent challenge in water systems.
The Role of Inhibitors
To mitigate the impacts of scale and corrosion, industries utilize various inhibitors
. These are chemical agents that are added to water systems to prevent or reduce the formation of scale and to protect metal surfaces from corrosion. Inhibitors can be classified into different categories based on their mechanism of actionscale and corrosion inhibitor
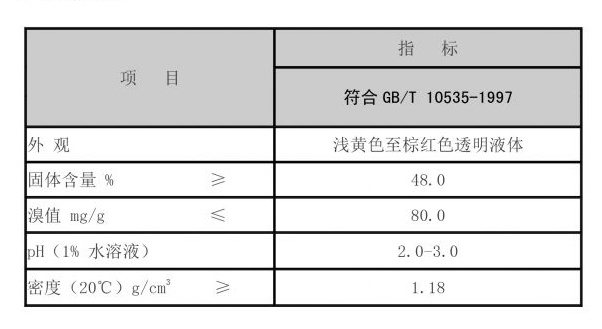
1. Scale Inhibitors These chemicals function by altering the crystallization process of minerals. By stabilizing the soluble forms of scale-forming compounds, they prevent the precipitation of minerals. Commonly used scale inhibitors include phosphonates, polyacrylic acids, and sodium hexametaphosphate, which are effective in both hard and soft water conditions. 2. Corrosion Inhibitors These substances work by forming a protective film on the surface of metals, thus preventing direct contact with corrosive agents. They can be organic or inorganic, with organic inhibitors like amines and phosphates being particularly popular in industrial applications. These compounds not only protect metal surfaces but also can enhance the overall efficiency of the system by reducing maintenance needs.
3. Combined Inhibitors Some formulations combine both scale and corrosion inhibition properties, offering a dual approach to system protection. These multi-functional inhibitors simplify treatment regimens and improve overall system performance.
Implementation Strategies
The successful application of scale and corrosion inhibitors requires careful consideration of several factors. First, it's essential to conduct a thorough analysis of the water chemistry to determine the specific types of scale and corrosion issues present. This assessment will guide the selection of the most appropriate inhibitors for the specific application.
Additionally, continuous monitoring and adjustment are crucial. Operating conditions such as temperature, pressure, and flow rates can fluctuate, which may affect the effectiveness of the inhibitors. Implementing real-time monitoring systems can help detect changes in water chemistry and allow for timely adjustments to treatment programs.
Conclusion
In summary, scale and corrosion inhibitors are vital components in the management of industrial water systems. By preventing the formation of scale and protecting metal surfaces from corrosion, these chemical agents enhance the efficiency, reliability, and lifespan of equipment. As industries continue to prioritize sustainability and operational efficiency, the role of inhibitors will become increasingly important. Properly implementing a comprehensive treatment strategy involving scale and corrosion inhibitors not only protects assets but also supports overall environmental and economic goals, ensuring a more sustainable industrial future.
-
lk-319-special-scale-and-corrosion-inhibitor-for-steel-plants-advanced-solutions-for-industrial-water-systemsNewsAug.22,2025
-
flocculant-water-treatment-essential-chemical-solutions-for-purification-processesNewsAug.22,2025
-
isothiazolinones-versatile-microbial-control-agents-for-industrial-and-consumer-applicationsNewsAug.22,2025
-
scale-inhibitor-key-solutions-for-water-system-scale-preventionNewsAug.22,2025
-
organophosphonates-versatile-scale-inhibitors-for-industrial-water-systemsNewsAug.22,2025
-
scale-and-corrosion-inhibitor-essential-chemical-solutions-for-water-system-maintenanceNewsAug.22,2025





