Amphoteric Polyacrylamide Applications and Benefits in Industry and Environmental Solutions
Amphoteric Polyacrylamide A Versatile Polymer in Modern Applications
Amphoteric polyacrylamide (APAM) is an advanced polymer that has garnered significant attention in various fields due to its unique properties. As a derivative of polyacrylamide (PAM), which is commonly used in water treatment, agriculture, and oil recovery, APAM boasts both positive and negative charge functionalities. This dual-characteristic enables APAM to interact with a wide range of substances, making it a versatile material in many industrial applications.
Structure and Properties
The chemical structure of amphoteric polyacrylamide comprises acrylamide monomers, which are modified to include both cationic (positively charged) and anionic (negatively charged) groups. This amphoteric nature allows APAM to adapt its behavior in response to varying pH levels and ionic strengths in the surrounding environment. As a result, APAM can easily flocculate and stabilize colloids, playing a crucial role in processes such as sedimentation and filtration.
Applications in Water Treatment
One of the most prominent applications of amphoteric polyacrylamide is in water treatment processes
. Due to its ability to bridge particles together, APAM is an effective flocculant for removing suspended solids and impurities from wastewater. When added to water, the polymer can neutralize charges on particles, leading them to aggregate into larger flocs that can be easily removed through sedimentation or filtration. This property is particularly valuable in treating industrial effluents, municipal wastewater, and drinking water.The use of APAM in water treatment not only enhances the clarity of the water but also improves the efficiency of the overall treatment process. Compared to traditional coagulants, APAM can work effectively over a broader range of conditions, making it a preferred choice for many treatment facilities.
Role in Agriculture
amphoteric polyacrylamide
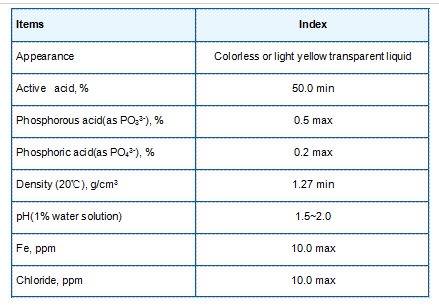
In agriculture, amphoteric polyacrylamide is utilized as a soil conditioner and water retention agent. By improving soil structure, APAM enhances water retention in arid and semi-arid regions, promoting sustainable agricultural practices. The polymer facilitates the formation of stable soil aggregates, which in turn improves aeration, root growth, and nutrient availability.
APAM's ability to enhance water retention is particularly beneficial in drip irrigation systems, where it helps minimize runoff and maximizes water usage efficiency. Furthermore, the presence of APAM in soil can reduce erosion and nutrient leaching, leading to healthier crops and increased yields.
Oil Recovery Enhancement
Amphoteric polyacrylamide is also employed in the oil and gas industry, particularly in enhanced oil recovery (EOR) processes. In this context, APAM is used to improve the mobility of oil by altering the viscosity of the injecting fluid. By incorporating APAM into water flooding processes, operators can achieve better oil displacement and recovery rates.
The amphoteric nature of APAM allows it to stabilize emulsions and reduce interfacial tension between oil and water, leading to more effective oil recovery. As a result, APAM contributes to maximizing the extraction efficiency of existing oil reservoirs, which is vital for meeting global energy demands.
Future Outlook
As environmental concerns grow and the demand for efficient resource management increases, the relevance of amphoteric polyacrylamide will likely expand across various sectors. Ongoing research aims to develop new formulations and improve the efficacy of APAM in diverse applications, from advanced waste management solutions to innovative agricultural practices.
In conclusion, amphoteric polyacrylamide stands out as a multifunctional polymer with diverse applications in water treatment, agriculture, and oil recovery. Its unique properties enable effective interactions with a variety of materials, making it an essential component in addressing modern environmental and resource challenges. As industries continue to pursue more sustainable practices, the role of APAM is poised to become even more prominent, ensuring a robust response to the demands of the future.
-
lk-319-special-scale-and-corrosion-inhibitor-for-steel-plants-advanced-solutions-for-industrial-water-systemsNewsAug.22,2025
-
flocculant-water-treatment-essential-chemical-solutions-for-purification-processesNewsAug.22,2025
-
isothiazolinones-versatile-microbial-control-agents-for-industrial-and-consumer-applicationsNewsAug.22,2025
-
scale-inhibitor-key-solutions-for-water-system-scale-preventionNewsAug.22,2025
-
organophosphonates-versatile-scale-inhibitors-for-industrial-water-systemsNewsAug.22,2025
-
scale-and-corrosion-inhibitor-essential-chemical-solutions-for-water-system-maintenanceNewsAug.22,2025





