corrosion scale inhibitor
Corrosion Scale Inhibitors An Essential Component in Industrial Applications
Corrosion is a natural process that leads to the deterioration of materials due to environmental factors, and it poses significant challenges across various industries, from oil and gas to water treatment and manufacturing. The impacts of corrosion are not only financial, accounting for billions in losses annually, but they also pose safety risks, environmental concerns, and operational inefficiencies. To combat this pervasive issue, corrosion scale inhibitors have emerged as an essential component in protecting infrastructure and machinery.
Understanding Corrosion and Its Effects
Corrosion can occur in various forms, including uniform corrosion, pitting corrosion, galvanic corrosion, and crevice corrosion, among others. When metal surfaces contact moisture, oxygen, and harmful ions, they undergo electrochemical reactions that degrade their structural integrity. For industries reliant on metal components, such as pipelines, boilers, and tanks, preventing corrosion is crucial to ensuring reliability and extending the lifespan of equipment.
The consequences of corrosion are substantial. They include costly repairs, increased downtime, and even catastrophic failures, which can lead to accidents and environmental disasters. Hence, developing effective strategies to inhibit corrosion is critical for maintaining operational efficiency and safety.
The Role of Corrosion Scale Inhibitors
Corrosion scale inhibitors are chemical substances designed to slow down or prevent the corrosion process. They function by forming a protective film over the metal surface, reducing its exposure to corrosive agents. These inhibitors can be categorized into several types
1. Film-Forming Inhibitors These chemicals create a thin barrier on the surface of metals, shielding them from corrosive elements. Examples include phosphates and silicates.
2. Anodic Inhibitors These compounds impede the oxidation process of metals, which is a critical reaction in corrosion. They are particularly effective in acidic environments.
3. Cathodic Inhibitors These work by decreasing the cathodic reaction that occurs during corrosion. They are often used in conjunction with anodic inhibitors to provide a comprehensive protective strategy.
4. Mixed Inhibitors These address both anodic and cathodic reactions, making them versatile options for a range of applications.
corrosion scale inhibitor
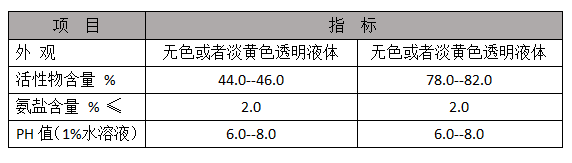
Among the inhibitors available, organic inhibitors are widely used due to their effectiveness, cost-efficiency, and low environmental impact. They often contain amines, acids, or surfactants that enhance their ability to form protective films on metal surfaces.
Application of Inhibitors
In the industrial realm, the application of corrosion scale inhibitors is tailored to specific environments. For instance, in oil and gas extraction, inhibitors are employed to mitigate corrosion in pipelines susceptible to wet sour environments. In cooling water systems, scale inhibitors are combined with biocides to prevent both scale formation and biological fouling that could lead to corrosion.
Moreover, in the construction of offshore structures, inhibitors are essential for protecting steel against seawater, which is an extremely corrosive medium. The aviation industry also employs specialized inhibitors to protect aircraft components from corrosion due to moisture and de-icing chemicals.
Environmental Considerations
While corrosion scale inhibitors are beneficial for extending the lifespan of various infrastructures, there are environmental considerations associated with their use. The potential toxicity of certain inhibitors, especially heavy metals, necessitates careful selection and monitoring to prevent detrimental effects on ecosystems. As a result, many companies are transitioning to environmentally friendly alternatives that maintain performance while minimizing ecological impact.
Future Trends
As industries continue to evolve, so too will the approaches to corrosion management. Future trends in corrosion scale inhibitors are likely to emphasize nanotechnology, smart coatings, and bioinspired materials that offer enhanced protective properties with minimal environmental footprint. Research into biodegradable inhibitors is gaining traction, aiming to provide effective corrosion protection without long-term harm to the environment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, corrosion scale inhibitors play a vital role in protecting industrial assets from the detrimental effects of corrosion. By understanding the mechanisms behind corrosion and strategically applying inhibitors, industries can mitigate risks, reduce costs, and promote safety. As technology advances and environmental awareness increases, the future of corrosion management looks promising, paving the way for innovative solutions that balance industrial needs with ecological responsibility.
-
lk-319-special-scale-and-corrosion-inhibitor-for-steel-plants-advanced-solutions-for-industrial-water-systemsNewsAug.22,2025
-
flocculant-water-treatment-essential-chemical-solutions-for-purification-processesNewsAug.22,2025
-
isothiazolinones-versatile-microbial-control-agents-for-industrial-and-consumer-applicationsNewsAug.22,2025
-
scale-inhibitor-key-solutions-for-water-system-scale-preventionNewsAug.22,2025
-
organophosphonates-versatile-scale-inhibitors-for-industrial-water-systemsNewsAug.22,2025
-
scale-and-corrosion-inhibitor-essential-chemical-solutions-for-water-system-maintenanceNewsAug.22,2025





