bit isothiazolinone
Understanding Bit Isothiazolinone A Multifaceted Preservative
In the realm of chemical preservatives, Bit isothiazolinone stands out as a subject of interest not only for its efficacy in preventing microbial growth but also due to its application across various industries, such as cosmetics, paints, and construction materials. Let's delve into what Bit isothiazolinone is, its uses, safety considerations, and the regulations surrounding its application.
What is Bit Isothiazolinone?
Bit isothiazolinone, often referred to in the industry as BIT or 2-n-butyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one, is a synthetic biocide belonging to the isothiazolinone class of compounds. These compounds are characterized by their ability to inhibit the growth of bacteria, fungi, and other microorganisms, making them invaluable in formulations where preservation and prolonged shelf life are critical. BIT is particularly effective against a broad spectrum of bacteria and molds, making it a popular choice in settings where hygiene and cleanliness are paramount.
Applications of Bit Isothiazolinone
Bit isothiazolinone finds application in numerous sectors. In the cosmetics industry, it is often used in creams, lotions, and shampoos. Its antimicrobial properties help prevent contamination and spoilage, ensuring that products remain safe for consumer use. Additionally, BIT can be found in household cleaning products, where it serves a similar purpose—acting as a protective agent against microbial growth.
In the construction industry, BIT is used in paints and coatings to prevent the formation of mold and mildew. The longevity of these products is crucial, especially in humid environments where mold growth is rampant. With BIT’s capability to inhibit such microbes, it plays a critical role in maintaining the aesthetic and structural integrity of buildings.
Moreover, BIT is also used in industrial applications, notably in cooling waters, paper manufacturing, and oilfield services, where its ability to combat bacterial and algal growth is essential to maintaining operational efficiency.
bit isothiazolinone
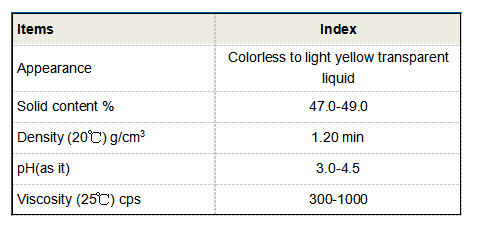
Safety and Regulatory Considerations
While Bit isothiazolinone is widely used, it is important to address concerns about its safety. Research has indicated that BIT can be a skin sensitizer, leading to allergic reactions in some individuals. This concern has prompted various regulatory bodies to establish guidelines for its use.
In Europe, the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) has classified BIT under the Biocidal Products Regulation (BPR). This classification mandates that products containing BIT are assessed for efficacy and safety before being made available to consumers. The maximum allowable concentration for BIT in consumer products has been established to minimize potential risks associated with exposure.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) also regulates BIT under the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA). The EPA has conducted assessments to ensure that BIT, when used according to established guidelines, does not pose significant health risks. Manufacturers are expected to follow stringent safety protocols, including proper labeling and usage instructions, to mitigate any potential adverse effects.
Conclusion
Bit isothiazolinone is a potent biocide that plays an integral role in preserving the quality and safety of a wide range of products. Its application in industries such as cosmetics, cleaning solutions, and construction underscores its versatility and usefulness. However, the potential for skin sensitization and allergic reactions warrants careful consideration and adherence to regulatory guidelines.
As the conversation around chemical safety continues to evolve, it is vital for both manufacturers and consumers to stay informed about the properties and regulations surrounding substances like Bit isothiazolinone. By understanding these factors, we can better navigate the complexities of chemical use in everyday products, ultimately leading to smarter choices that prioritize safety and efficacy.
-
Pbtc Scale InhibitorPBTC: A Scale Protector for Industrial Water TreatmentNewsAug.05,2025
-
Organic Phosphonate: An Efficient Defender in the Field of Scale InhibitionNewsAug.05,2025
-
Hydrolyzed Polymaleic Anhydride: Green Pioneer in Scale Inhibition FieldNewsAug.05,2025
-
PAPEMP Polyamino Polyether Methylene Phosphonic Acid For SaleNewsAug.05,2025
-
Flocculant Water Treatment: A Pioneer in Purification in the Field of Water TreatmentNewsAug.05,2025
-
Benzyl Isothiazolinone: An Efficient and Broad-Spectrum Antibacterial Protective GuardNewsAug.05,2025





