industrial flocculant
The Role of Industrial Flocculants in Water Treatment Processes
In recent years, the demand for clean water has surged, driving innovations in water treatment processes across various industries. One key player in this field is the use of industrial flocculants. These agents play a significant role in enhancing the efficiency of water purification, wastewater treatment, and other related applications. This article delves into the importance of industrial flocculants, how they work, and their impact on environmental sustainability.
What are Industrial Flocculants?
Flocculants are substances that promote the agglomeration of fine particulates in liquid, leading to the formation of larger particles, or flocs, that can be easily removed. They are commonly used in the treatment of industrial wastewater, municipal sewage, and even in the processing of drinking water. Typically, flocculants can be categorized into synthetic and natural types. Synthetic flocculants include polyacrylamides and other polymer-based materials, while natural flocculants are derived from plant or animal sources, such as starches and proteins.
How Do Flocculants Work?
The flocculation process begins with the addition of a flocculant to the liquid medium that needs treatment. The flocculant molecules interact with suspended particles in the water due to their charge properties. Essentially, flocculants can be ionic or non-ionic, with ionic types being more effective in certain contexts.
1. Charge Neutralization Many suspended particles carry a negative charge that prevents them from coagulating. Flocculants neutralize this charge, allowing the particles to come closer together. 2. Bridge formation After the charge is neutralized, the flocculant molecules can act as a ‘bridge’ between particles, facilitating the formation of flocs.
industrial flocculant
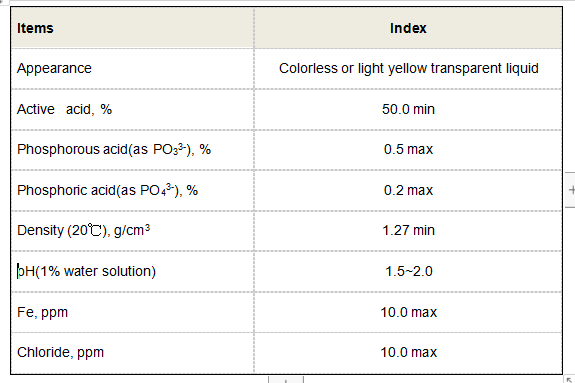
Applications of Industrial Flocculants
The applications of industrial flocculants are diverse, ranging from mining and mineral processing to food production and construction. In the mining industry, flocculants are crucial for separating valuable minerals from waste material, improving recovery rates, and reducing environmental impact. In wastewater treatment, they enhance the removal of solids, leading to compliance with regulatory standards and protection of aquatic ecosystems.
Moreover, in the food industry, flocculants are employed to clarify juices, wines, and other beverages, contributing to the aesthetic and quality attributes of these products. They also play a role in the paper industry by aiding in the processing and recycling of fiber materials.
Environmental Benefits and Sustainability
The use of flocculants presents significant environmental benefits. Proper treatment of wastewater minimizes the impact on natural water bodies, helping to protect aquatic life and ecosystems. By improving the efficiency of resource recovery during industrial processes, flocculants contribute to the principles of circular economy.
Additionally, advancements in bio-based flocculants are paving the way for more sustainable practices. As industries turn towards greener alternatives, natural flocculants are gaining attention for their biodegradability and lower toxicity compared to synthetic counterparts.
Conclusion
Industrial flocculants are essential in today's efforts to achieve effective water treatment and pollution control. Their ability to enhance sedimentation processes and improve water quality makes them invaluable across various sectors. As industries continue to prioritize sustainability, the development and adoption of efficient and eco-friendly flocculants will play a pivotal role in ensuring clean water for future generations. Embracing these innovations, while also paying attention to environmental impacts, will be key as we move forward in the quest for a healthier planet.
-
lk-319-special-scale-and-corrosion-inhibitor-for-steel-plants-advanced-solutions-for-industrial-water-systemsNewsAug.22,2025
-
flocculant-water-treatment-essential-chemical-solutions-for-purification-processesNewsAug.22,2025
-
isothiazolinones-versatile-microbial-control-agents-for-industrial-and-consumer-applicationsNewsAug.22,2025
-
scale-inhibitor-key-solutions-for-water-system-scale-preventionNewsAug.22,2025
-
organophosphonates-versatile-scale-inhibitors-for-industrial-water-systemsNewsAug.22,2025
-
scale-and-corrosion-inhibitor-essential-chemical-solutions-for-water-system-maintenanceNewsAug.22,2025





