polymaleic anhydride
Polymaleic Anhydride A Versatile Polymer in Modern Applications
Polymaleic anhydride (PMA) is a polymer that has garnered significant attention in various fields due to its unique properties and versatility. This polymer, formed through the polymerization of maleic anhydride, is characterized by its anhydride functional groups, which bestow it with unique chemical reactivity and physical properties that make it suitable for a myriad of applications.
Chemical Structure and Properties
PMA is a linear polymer comprising repeating units of maleic anhydride. Its structure allows for the formation of various copolymers and derivatives by incorporating different monomers. The anhydride functional groups in PMA are highly reactive, allowing the polymer to undergo further chemical modifications, such as hydrolysis, amidation, and esterification. This reactivity makes PMA a valuable platform for designing functional materials.
The physical properties of PMA include excellent thermal stability and solubility in various solvents, which facilitate its application in industrial processes. Moreover, PMA has a high glass transition temperature, contributing to its stability at elevated temperatures. These characteristics render PMA suitable for use in environments that demand both durability and flexibility.
Applications in Industry
PMA finds its applications across several industries, including coatings, adhesives, and plastics. In the coatings sector, PMA is utilized as a binder due to its excellent adhesion capabilities. It can be used as a dispersant in water-based paints and coatings; its anhydride groups improve the wetting characteristics, leading to enhanced performance.
In the adhesive industry, PMA serves as a key component in formulating strong and durable adhesives. When combined with other polymers, it enhances the adhesive properties, providing better bonding strength and performance under diverse environmental conditions. The ability to modify PMA through copolymerization further expands its adhesive properties, allowing customization for specific applications.
polymaleic anhydride
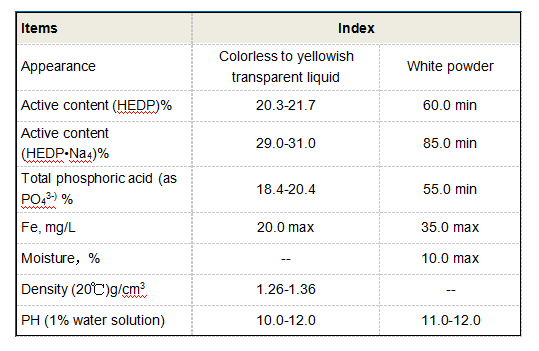
In the plastics industry, PMA is used as a processing aid and is often blended with other polymers to improve their processing characteristics. It can help enhance the flow properties of molten polymers during extrusion and injection molding processes. This property is particularly useful in the production of films and other plastic products, where uniform material flow is essential.
Biocompatibility and Biomedical Applications
One of the most notable advancements in the use of PMA is its application in the biomedical field. Researchers have discovered that PMA can be modified to create biocompatible materials suitable for drug delivery systems and tissue engineering scaffolds. The incorporation of PMA into biomedical devices addresses the growing demand for materials that can safely interact with biological systems.
PMA-based materials can be engineered to release therapeutic agents over time, providing controlled drug delivery for various medical treatments. The ability to tailor the release profiles, coupled with the nontoxic nature of the polymer, makes it an attractive candidate for developing advanced drug delivery systems.
Environmental Considerations
With increasing awareness of environmental issues, the development of sustainable materials has gained importance. PMA can be synthesized from renewable resources, making it a potential candidate for environmentally friendly materials. Its recyclability and potential for biodegradability, when formulated appropriately, align with the goals of reducing plastic waste and minimizing environmental impact.
Conclusion
Polymaleic anhydride is a remarkable polymer with a diverse range of applications across multiple industries. Its unique properties, including chemical reactivity, thermal stability, and the ability to form copolymers, make it a valuable material in coatings, adhesives, plastics, and biomedical applications. As research continues to explore the potential of PMA and its derivatives, we can expect to see innovative uses that address both industrial needs and environmental concerns. The future of PMA is promising, with the potential to contribute significantly to sustainable development and advanced technologies in various fields.
-
Understanding Polycarboxylic Acids: Properties, Applications, and Future PotentialNewsJul.28,2025
-
Scale Inhibitor Explained: How to Protect Your System from Limescale and Hard Water DamageNewsJul.28,2025
-
Scale and Corrosion Inhibitors: Essential Chemicals for Industrial Water System ProtectionNewsJul.28,2025
-
Polyaspartic Acid: A Biodegradable Polymer for Sustainable ChemistryNewsJul.28,2025
-
Isothiazolinones: A Versatile Antimicrobial Class with Industrial Power and Regulatory ChallengesNewsJul.28,2025
-
A Deep Dive into 2-Phosphonobutane-1,2,4-Tricarboxylic Acid (PBTC)NewsJul.28,2025





