polyacrylamide pdf
Polyacrylamide An Overview
Polyacrylamide (PAM) is a versatile polymer that has a wide range of applications across various industries, including water treatment, agriculture, mining, and cosmetics. Its unique properties make it an essential material for many processes, enhancing efficiency and effectiveness. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of polyacrylamide, including its composition, production, applications, and environmental considerations.
Composition and Production
Polyacrylamide is synthesized through the polymerization of acrylamide monomers. The process typically involves a radical polymerization method, often catalyzed by initiators, which can create either linear or cross-linked structures. The extent of cross-linking influences the physical properties of the final product, such as solubility and viscosity. The resulting polymer can be categorized into different forms, including anionic, cationic, and nonionic polyacrylamide, each tailored for specific applications based on the charge and molecular weight.
One of the significant advantages of polyacrylamide is its solubility in water, allowing it to dissolve readily and form viscous solutions. This feature plays a crucial role in its functionality across various applications, making it an ideal choice for water treatment processes, where it can act as a flocculant to aid in the removal of suspended solids and clarify water.
Applications in Various Industries
1. Water Treatment Polyacrylamide is widely used in municipal and industrial water treatment facilities. Its properties as a flocculant help to aggregate fine particles, facilitating their removal during sedimentation and filtration. This results in cleaner water, meeting safety and regulatory standards.
2. Agriculture In agriculture, PAM serves as a soil conditioner, improving water retention and reducing soil erosion. Farmers can employ polyacrylamide to enhance irrigation efficiency, particularly in arid regions where water scarcity is a significant challenge. Furthermore, it also helps in the successful establishment of crops by creating a more stable soil matrix.
polyacrylamide pdf
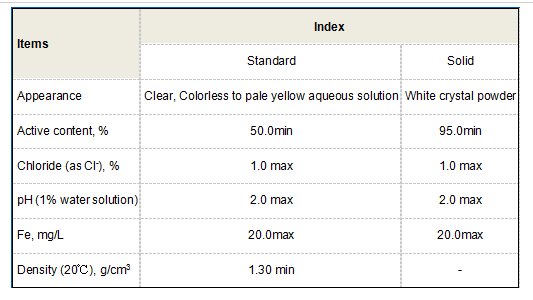
3. Mining The mining industry employs polyacrylamide for various applications, particularly in the extraction of minerals. It functions as a flocculant in the separation process, helping to clarify tailings and recycle water, which is essential for sustainable mining practices.
4. Cosmetics In the cosmetics industry, polyacrylamide is utilized in formulations as a thickening agent. Its ability to stabilize emulsions and improve the texture of products like creams, lotions, and gels has made it a popular ingredient in personal care items.
5. Biotechnology and Medicine Polyacrylamide gels are commonly used in electrophoresis, a technique for separating proteins and nucleic acids based on size. This application is critical for research and diagnostics in molecular biology.
Environmental Considerations
Despite its numerous benefits, the use of polyacrylamide has raised environmental concerns, particularly regarding its potential toxicity and persistence in the environment. Acrylamide, the monomer used in PAM production, is considered a potential neurotoxin and carcinogen. Therefore, strict regulations govern its use, particularly in drinking water applications. It is essential to ensure that the polymer is adequately treated and that its residuals do not pose a risk to human health or ecosystems.
Moreover, while polyacrylamide aids in reducing soil erosion and improving water retention, ongoing research is required to understand the long-term ecological impacts of its application. Sustainable practices must be developed to mitigate potential risks associated with its widespread use.
Conclusion
Polyacrylamide is a multifaceted polymer with significant contributions across various sectors, particularly in water treatment, agriculture, and industry. Its unique properties enable effective solutions to complex challenges. However, it is vital to remain mindful of its environmental implications and ensure that its applications are sustainable and safe. As research and technology evolve, the potential for polyacrylamide applications will continue to expand, offering innovative solutions to meet the demands of today’s world.
-
Pbtc Scale InhibitorPBTC: A Scale Protector for Industrial Water TreatmentNewsAug.05,2025
-
Organic Phosphonate: An Efficient Defender in the Field of Scale InhibitionNewsAug.05,2025
-
Hydrolyzed Polymaleic Anhydride: Green Pioneer in Scale Inhibition FieldNewsAug.05,2025
-
PAPEMP Polyamino Polyether Methylene Phosphonic Acid For SaleNewsAug.05,2025
-
Flocculant Water Treatment: A Pioneer in Purification in the Field of Water TreatmentNewsAug.05,2025
-
Benzyl Isothiazolinone: An Efficient and Broad-Spectrum Antibacterial Protective GuardNewsAug.05,2025





