Synthesis and Applications of Hydroxy Ethylidene Diphosphonic Acid in Industry
The Significance of Hydroxyethylidene Diphosphonic Acid (HEDP) in Various Industries
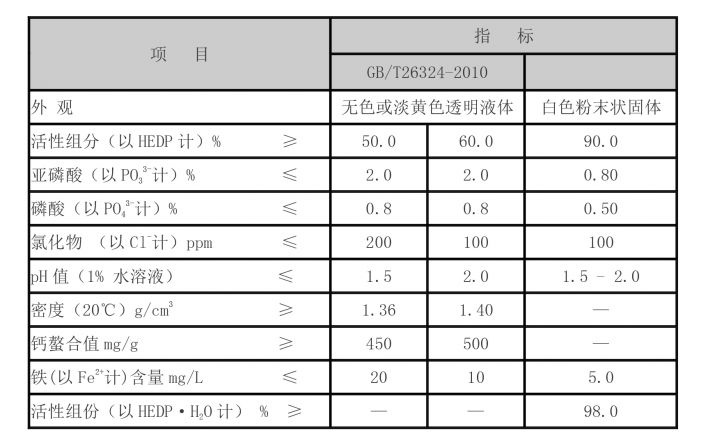
Hydroxyethylidene diphosphonic acid (HEDP) is a highly effective phosphonate compound that has found applications across various industries due to its remarkable properties. Commonly used as a scale inhibitor and dispersant, HEDP plays a crucial role in water treatment, metal surface treatment, and even in the manufacturing of ceramics. This article explores the chemical structure, properties, applications, and environmental impact of HEDP, particularly focusing on its 1% concentration usage.
Chemical Structure and Properties
HEDP is chemically known as 1-Hydroxyethylidene-1,1-diphosphonic acid. Its structure consists of a hydroxyl group and two phosphonic acid functional groups, making it a diphosphonic acid. The unique arrangement of these groups confers outstanding chelating properties, allowing HEDP to efficiently bind with metal ions. This affinity for divalent and trivalent metal ions is particularly important in preventing scale formation in industrial processes.
One of the key attributes of HEDP is its stability over a wide pH range, which allows it to maintain effectiveness in varied conditions. At a 1% concentration, HEDP demonstrates excellent scale inhibition and corrosion control, making it a popular choice in formulations for water treatment and industrial applications.
Applications in Water Treatment
HEDP is primarily used in water treatment processes, especially in cooling water systems, reverse osmosis systems, and industrial water circuits. In these environments, the formation of scale can severely hinder efficiency and equipment lifespan. HEDP effectively inhibits the precipitation of calcium carbonate, calcium sulfate, and other undesirable scales, thereby maintaining optimal performance of heat exchangers and cooling towers.
Moreover, because of its chelating ability, HEDP also helps in dispersing particulate matter and reducing fouling in water systems. This ensures not only the longevity of the systems but also lower maintenance costs and improved energy efficiency.
Metal Surface Treatment
In the field of metal surface treatment, HEDP serves as a critical component in cleaning and anti-corrosion formulations. It forms stable complexes with metal ions, preventing rust and corrosion during storage and use. HEDP is often incorporated into alkaline cleaners and rust removers, providing effective protection to metal surfaces against tarnishing and degradation.
1 hydroxy ethylidene 1 1 diphosphonic acid hedp1
The usage of HEDP in metalworking fluids aids in minimizing wear on machinery, enhancing the longevity of tools, and improving the overall efficiency of manufacturing processes.
Ceramics and Construction Materials
HEDP’s applications extend to the production of ceramics and construction materials. In the ceramic industry, it is used as a dispersant for glazes and body formulations, providing better flow and uniformity. The incorporation of HEDP aids in reducing aggregates and improving the product quality of ceramics by enhancing the dispersion of solid particles.
In construction, HEDP can be found in various formulations, including concrete admixtures, where it helps in improving workability and preventing the settling of particles in a cement mix.
Environmental Considerations
Despite its broad utility, the use of HEDP raises concerns regarding environmental safety. Its phosphonate structure can contribute to the phosphorous load in aquatic environments if not managed properly, potentially leading to eutrophication. Therefore, the proper dosage, such as the commonly used 1% concentration, plays a critical role in minimizing environmental impact while still offering the necessary benefits across applications.
To mitigate any negative effects, industries employing HEDP are encouraged to adopt sustainable practices and adhere to regulatory guidelines governing its use. Continuous research into alternative compounds and greener formulations is also a growing trend, aimed at reducing dependency on phosphonates while still achieving desired industrial outcomes.
Conclusion
Hydroxyethylidene diphosphonic acid is an indispensable compound in many industries, particularly due to its scale inhibiting and corrosion-fighting properties. Its diverse applications across water treatment, metal surface treatment, ceramics, and construction materials underline its significance. However, the environmental implications of its use necessitate responsible management and adherence to best practices. As industries continue to evolve, HEDP remains a critical component in ensuring operational efficiency while balancing environmental concerns.
-
Pbtc Scale InhibitorPBTC: A Scale Protector for Industrial Water TreatmentNewsAug.05,2025
-
Organic Phosphonate: An Efficient Defender in the Field of Scale InhibitionNewsAug.05,2025
-
Hydrolyzed Polymaleic Anhydride: Green Pioneer in Scale Inhibition FieldNewsAug.05,2025
-
PAPEMP Polyamino Polyether Methylene Phosphonic Acid For SaleNewsAug.05,2025
-
Flocculant Water Treatment: A Pioneer in Purification in the Field of Water TreatmentNewsAug.05,2025
-
Benzyl Isothiazolinone: An Efficient and Broad-Spectrum Antibacterial Protective GuardNewsAug.05,2025





