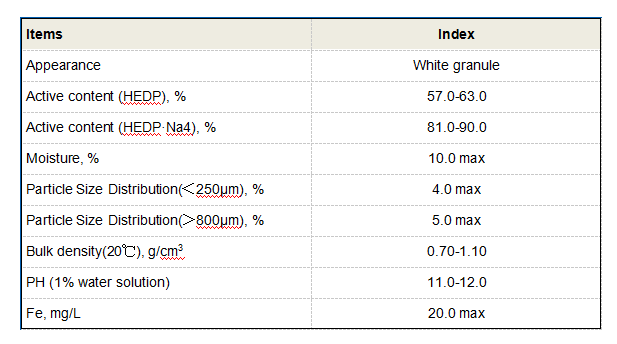
anionic polyacrylamide
Anionic Polyacrylamide A Versatile Polymer in Water Treatment and Beyond
Anionic polyacrylamide (APAM) is a water-soluble polymer known for its excellent flocculating and sedimentation properties. As a derivative of polyacrylamide, this polymer has anionic charges that give it unique characteristics and make it highly effective in various applications, especially in water treatment processes.
One of the primary uses of anionic polyacrylamide is in the field of wastewater treatment. This polymer acts as a flocculant, helping to aggregate suspended solids into larger particles, or flocs, which are easier to remove from water. By enhancing the sedimentation process, APAM plays a crucial role in clarifying water in municipal wastewater treatment facilities as well as in industrial operations. The increased efficiency in removing pollutants not only helps in complying with environmental regulations but also contributes to sustainable water management.
In addition to water treatment, APAM finds applications in the mining industry. It is used to improve the quality of water used in mineral processing and to help in the recovery of valuable minerals. APAM facilitates the separation of fine particles from solutions, which can significantly enhance the yield of extracted materials. This application highlights the polymer's economic benefits, as improved recovery rates can lead to cost savings for mining operations.
anionic polyacrylamide
Furthermore, anionic polyacrylamide is employed in the agricultural sector as a soil conditioner
. It enhances soil structure, improves water retention, and reduces soil erosion. By promoting better soil aeration and root penetration, APAM contributes to healthier plant growth, making it a valuable asset for farmers looking to improve crop yields. Its ability to bind soil particles also helps mitigate the effects of drought, providing an essential resource in regions susceptible to water scarcity.The versatility of anionic polyacrylamide extends to other industries as well, including oil recovery, cosmetics, and paper manufacturing. In enhanced oil recovery, APAM is injected into oil reservoirs to increase the viscosity of water and improve the displacement of oil. In cosmetics, it serves as a thickening agent and stabilizer in various formulations. The paper industry utilizes APAM to improve the retention of fibers and fillers during the production process, thereby enhancing paper quality.
Despite its numerous advantages, safe handling and environmental considerations are important with any chemical product, including anionic polyacrylamide. While it is generally considered to have low toxicity, proper guidelines must be followed to minimize any potential ecological impact. Research is ongoing to further understand the polymer's biodegradability and develop more sustainable alternatives.
In conclusion, anionic polyacrylamide is a multifaceted polymer that plays a critical role in a variety of industries, most notably in water treatment and agriculture. Its effectiveness in flocculation, soil conditioning, and operational enhancements positions it as a vital component for promoting sustainability and efficiency in modern practices. As research continues to evolve, we can expect even more innovative applications for this remarkable polymer, paving the way for increased environmental responsibility and improved resource management.
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





