Exploring the Chemical Properties and Uses of Butane-1,2,4-tricarboxylic Acid in Various Applications
Butane-1,2,4-Tricarboxylic Acid A Multifaceted Compound
Butane-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid, also known as citraconic acid, is a naturally occurring organic compound that has garnered interest due to its various applications in chemistry, biology, and industry. This acid is an important tricarboxylic acid that features three carboxyl functional groups (-COOH) attached to a butane backbone. The molecular formula of butane-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid is C7H10O6, and its importance in different fields makes it a compelling subject of study.
Butane-1,2,4-Tricarboxylic Acid A Multifaceted Compound
In the realm of chemistry, butane-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid is recognized for its ability to serve as a multifunctional building block. The presence of three carboxyl groups allows for a wide range of potential reactions, including esterification, amidation, and decarboxylation. These reactions make butane-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid a valuable intermediate in the production of polymeric materials, surfactants, and additives. By modifying the carboxyl groups, chemists can tailor the properties of the resulting compounds for specific applications, enhancing their utility in various industrial processes.
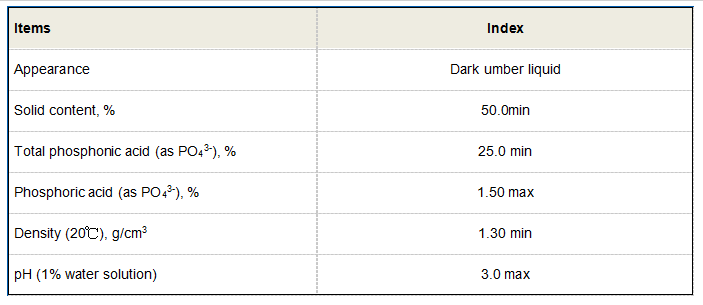
butane 1 2 4 tricarboxylic acid
Moreover, the significance of butane-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid extends to environmental chemistry. As an organic acid, it can play a role in various ecological processes such as soil chemistry and nutrient availability. It has been studied for its potential applications in bioremediation, where its capability to chelate metals might aid in the detoxification of contaminated environments. Understanding how this compound interacts with different pollutants can help develop more effective strategies to restore ecological balance.
Furthermore, the agricultural sector has also embraced butane-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid due to its potential as a bio-stimulant. Research has shown that this compound can enhance plant growth by improving nutrient uptake and fostering beneficial microbial activities in the soil. As agriculture shifts towards more sustainable practices, incorporating natural compounds like butane-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid may contribute to healthier ecosystems and improved crop yields without relying heavily on synthetic fertilizers.
In summary, butane-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid is a versatile compound with a myriad of applications across various fields. Its role in biological processes, chemical reactions, environmental sustainability, and agriculture underscores its importance as a multifunctional agent. As research continues to unveil the potential of this organic acid, it promises to play an increasingly vital role in both scientific innovation and practical applications. Understanding its properties and reactivity will enable further advancements that can benefit health, industry, and the environment alike.
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





