pbtca
Understanding PBTCA A Comprehensive Overview
PBTCA, or phosphonobutane-tricarboxylic acid, is a versatile organic compound with significant applications in various fields, particularly in water treatment and the formulation of complex chemicals. As an effective chelating agent, PBTCA plays a crucial role in controlling scale and corrosion in industrial processes, making it a vital component in maintaining the efficiency and longevity of equipment.
One of the primary characteristics of PBTCA is its ability to bind metal ions, which are often present in water systems. These metal ions, such as calcium, magnesium, and iron, can lead to undesirable scale formation on pipes and machinery. When scale accumulates, it inhibits the flow of water and reduces the efficiency of heat exchangers, leading to increased energy consumption and operational costs. By introducing PBTCA into the system, these metal ions are effectively sequestered, preventing the formation of scale and ensuring smoother operation.
.
The synthesis of PBTCA involves a series of chemical reactions, where simple organic compounds are combined in the presence of catalysts and specific conditions to yield the final product. The resulting compound features multiple carboxylic acid groups, which are responsible for its exceptional chelating ability. The structural configuration of PBTCA allows it to interact effectively with various ions, thereby enhancing its functionality in diverse applications.
pbtca
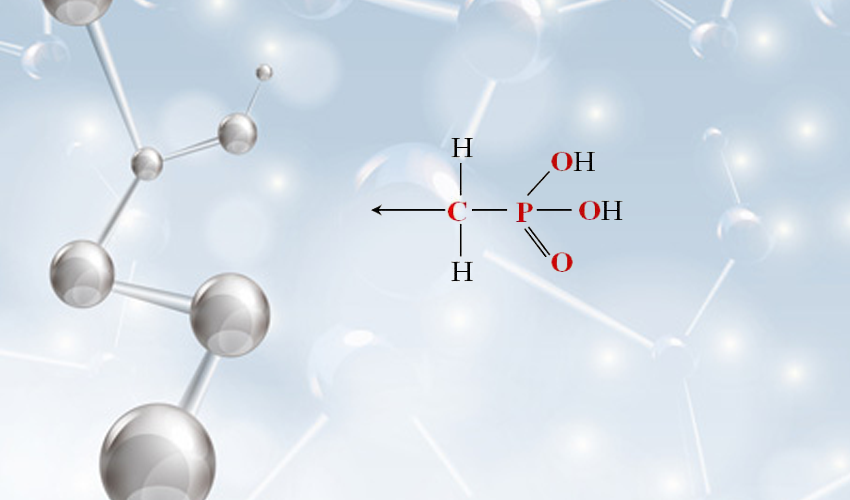
PBTCA's significance extends beyond merely being an industrial chemical. In the realm of agriculture, PBTCA is sometimes incorporated into fertilizer formulations to improve nutrient uptake in plants. By chelating essential micronutrients, such as zinc and iron, PBTCA enhances their bioavailability, leading to better growth and yield of crops. This aspect of PBTCA is particularly important in regions with nutrient-deficient soils, where maximizing agricultural productivity is crucial for food security.
In the context of environmental sustainability, PBTCA offers a more eco-friendly alternative to traditional phosphonates. As industries seek to reduce their environmental impact, the demand for biodegradable and low-toxicity chemicals like PBTCA has grown. Unlike some conventional phosphonates, which can contribute to eutrophication in water bodies, PBTCA's biodegradability ensures that it poses a lower risk to aquatic ecosystems.
Moreover, ongoing research into the properties and applications of PBTCA continues to unveil new potential uses. Its effectiveness in formulating detergents and cleaning agents, for instance, is an area of great interest. The ability to stabilize formulations and enhance cleaning power through chelation makes PBTCA a valuable ingredient in consumer products.
In conclusion, PBTCA stands out as a multifaceted compound with essential applications in water treatment, agriculture, and cleaning formulations. Its unique properties as a chelating agent not only help prevent scale and corrosion in industrial systems but also contribute to improved agricultural practices and environmentally friendly solutions. As industries and researchers explore innovative ways to utilize PBTCA, its significance in promoting efficiency and sustainability is likely to increase, reinforcing its role as a critical component in modern chemical applications. With its broad applicability and environmental benefits, PBTCA is set to remain an important player in the chemical industry for years to come.
-
LK-319 Special Scale And Corrosion Inhibitor For Steel Plants: Advanced Solutions for Industrial Water SystemsNewsAug.22,2025
-
Flocculant Water Treatment: Essential Chemical Solutions for Purification ProcessesNewsAug.22,2025
-
Isothiazolinones: Versatile Microbial Control Agents for Industrial and Consumer ApplicationsNewsAug.22,2025
-
Scale Inhibitor: Key Solutions for Water System Scale PreventionNewsAug.22,2025
-
Organophosphonates: Versatile Scale Inhibitors for Industrial Water SystemsNewsAug.22,2025
-
Scale and Corrosion Inhibitor: Essential Chemical Solutions for Water System MaintenanceNewsAug.22,2025





