water coagulation and flocculation
Water Coagulation and Flocculation A Key Process in Water Treatment
Water treatment is essential for ensuring that water is safe for human consumption and environmental sustainability. Two critical processes in water treatment are coagulation and flocculation. These processes help in removing suspended solids, colloids, and impurities from water, thereby improving its quality.
Coagulation Process
Coagulation is the first step in the treatment of water that involves adding coagulants to destabilize suspended particles. Common coagulants include aluminum sulfate (alum), ferric chloride, and polyaluminum chloride. When these chemicals are mixed with water, they form positively charged ions that neutralize the negative charges of the suspended particles, including silt, clay, and organic matter. As the particles lose their negative charges, they begin to clump together, a process known as aggregation.
The effectiveness of coagulation depends on various factors, such as pH, temperature, and the concentration of the coagulant used
. Maintaining optimal conditions is essential to ensure that the coagulated particles can effectively combine and settle out of the water.Flocculation Process
Following coagulation, flocculation is employed to further enhance the removal of particles from water. In this phase, gentle stirring or agitation is applied to encourage the formation of larger aggregates or 'flocs' from the smaller coagulated particles created in the previous step. Flocculants, such as polyacrylamides or natural compounds like starch, may be added to facilitate the floc formation process.
water coagulation and flocculation
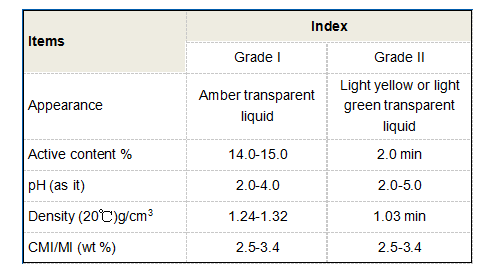
The key objective of flocculation is to create larger particles that can easily settle at the bottom of the treatment tank. This is achieved through slow mixing, which allows time for the smaller aggregates to collide and bond together, ultimately forming larger flocs that can be separated from the water more efficiently during the sedimentation phase.
Importance in Water Treatment
The combination of coagulation and flocculation plays a vital role in removing impurities from drinking water. This process not only improves water clarity by reducing turbidity but also helps in mitigating harmful microorganisms and chemical contaminants. By effectively removing these undesirable substances, coagulation and flocculation contribute significantly to public health protections.
Moreover, these processes can also be used in various industrial applications, such as wastewater treatment and the treatment of surface water for various purposes. The principles of coagulation and flocculation extend beyond drinking water treatment, playing an essential role in ensuring clean water for agriculture, recreation, and industrial use.
Conclusion
In summary, coagulation and flocculation are integral components of the water treatment process, combining chemistry and engineering to enhance water quality. By understanding and optimizing these processes, we can ensure a safe, clean water supply for communities and protect our natural resources for future generations. As the global demand for clean water continues to rise, the importance of these processes in water treatment will become increasingly crucial in addressing the challenges of water scarcity and contamination.
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





