Advancements in Polyacrylamide Production Techniques and Applications for Industry Growth
The Production of Polyacrylamide An Overview
Polyacrylamide (PAM) is a versatile synthetic polymer widely used in various industrial applications, ranging from water treatment to agriculture. Its production involves polymerization of acrylamide monomers, and understanding this process is crucial for improving efficiency and ensuring environmental safety.
Key Steps in Polyacrylamide Production
The production of polyacrylamide generally involves several critical steps acrylamide synthesis, polymerization, and post-production processing
.1. Acrylamide Synthesis Acrylamide is produced from acrylic acid and ammonia through a process known as ammonolysis. This step is pivotal as the quality of acrylamide directly affects the characteristics of the final polymer. Efforts to optimize this process focus on increasing yield and minimizing the formation of impurities, particularly the potentially hazardous by-product, acrylamide, which poses health risks.
2. Polymerization After synthesizing acrylamide, the next key step is the polymerization process, which can occur through various methods, including free radical polymerization and solution polymerization. Free radical polymerization involves the initiation of a chemical reaction by free radicals, leading to the formation of long chains of polymer. The conditions of polymerization—such as temperature, pressure, and the presence of catalysts—must be carefully controlled to produce polyacrylamide with the desired molecular weight and properties.
3. Post-Production Processing Once polymerization is complete, the resulting polyacrylamide needs to be processed for its target application. Depending on its end-use, PAM can be produced in different forms, including powders, emulsions, and solutions. The drying process, particle size distribution adjustment, and stabilization against degradation are essential steps to ensure that the polyacrylamide retains its functionality and effectiveness during use.
polyacrylamide production
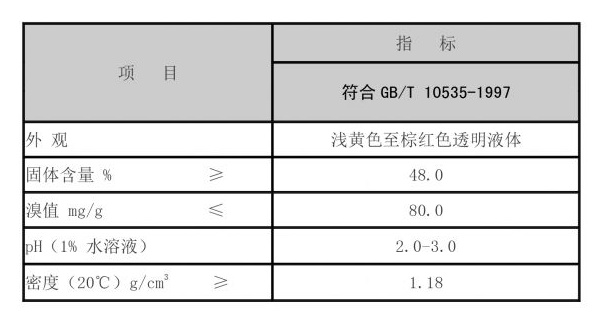
Applications of Polyacrylamide
Polyacrylamide's unique properties—such as high water retention capacity and non-toxicity—make it an ideal candidate for a variety of applications. In water treatment, PAM is valuable for clarifying water by facilitating the aggregation of suspended particles, aiding in easier removal during filtration processes. Its use in agriculture includes soil conditioning, where it enhances water retention in arid regions, thus promoting healthy crop growth.
In the oil and gas industry, polyacrylamide is utilized in enhanced oil recovery during the drilling process, as it helps to increase the efficiency of oil extraction. The paper-making industry also benefits from PAM’s ability to improve retention of fines and fillers, enhancing the quality of the final product.
Environmental Considerations
While the applications of polyacrylamide are beneficial, there are environmental and safety considerations associated with its production and use. The handling of acrylamide, being a neurotoxin, requires strict regulatory compliance to minimize exposure risks to workers. Additionally, efforts are being made to develop greener production methods, reducing the environmental impact associated with traditional polymerization processes.
In conclusion, the production of polyacrylamide is a complex process that plays a crucial role in numerous industries. By optimizing production methods and prioritizing safety and environmental sustainability, the industry can continue to benefit from this valuable polymer while mitigating its potential risks. As research and technology advance, the future of polyacrylamide production looks promising, paving the way for more sustainable practices and diverse applications.
-
2 Phosphonobutane 1,2,4 Tricarboxylic Acid (PBTCA): Superior Scale & Corrosion InhibitorNewsAug.31,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride: High-Purity DisinfectantNewsAug.30,2025
-
2-Phosphonobutane-1,2,4-Tricarboxylic Acid: Scale & CorrosionNewsAug.29,2025
-
Premium Isothiazolinones | Broad-Spectrum Biocidal SolutionsNewsAug.28,2025
-
LK-319 Special Scale And Corrosion Inhibitor For Steel Plants: Advanced Solutions for Industrial Water SystemsNewsAug.22,2025
-
Flocculant Water Treatment: Essential Chemical Solutions for Purification ProcessesNewsAug.22,2025





