Synthesis and Applications of Amino Tri Methylene Phosphonic Acid in Modern Chemistry
Amino Tri Methylene Phosphonic Acid An Overview
Amino tri methylene phosphonic acid (ATMP) is an influential compound in the fields of chemistry and material science, particularly known for its remarkable chelating properties and versatility as a scale inhibitor. This article delves into the structure, properties, applications, and significance of ATMP, highlighting its essential role in various industrial processes.
Chemical Structure and Properties
ATMP, chemically represented as C4H15N2O9P, consists of three methylene groups, an amino group, and a phosphonic acid functional group. Its molecular structure is characterized by a central phosphorus atom bound to a methylene chain and an amino group, which grants ATMP its aqueous solubility and strong chemical reactivity.
One of the defining features of ATMP is its ability to form stable complexes with metal ions. The phosphonic acid groups demonstrate a high affinity for binding with divalent and trivalent metal ions, such as calcium, magnesium, and iron. This chelation process not only inhibits the precipitation of scale-forming minerals but also enhances the stability of various aqueous solutions.
Applications in Industry
ATMP is widely utilized in water treatment formulations due to its effectiveness in preventing scale formation in cooling towers, boilers, and evaporators. The compound is particularly valuable in industries that face challenges related to limescale buildup, which can significantly impair efficiency and increase maintenance costs. By incorporating ATMP into water treatment systems, industries can achieve better control over scaling, thereby ensuring smoother operations and prolonging equipment lifespan.
amino tri methylene phosphonic acid
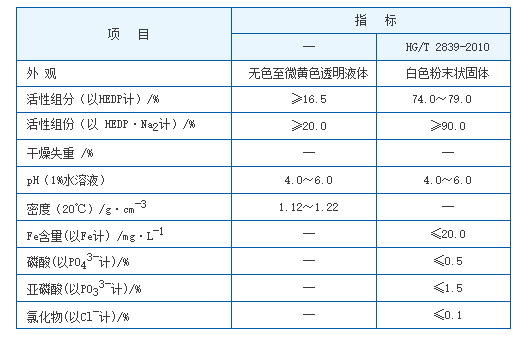
In addition to water treatment, ATMP finds application in the textile and dye industries. Here, its chelating properties help achieve better dye fixation, improving color yield and consistency while reducing the environmental impact of wastewater. Moreover, ATMP is employed in the formulation of detergents and cleaning agents, where it promotes the solubilization of hard water ions, enhancing the overall cleaning process.
ATMP's role in oil and gas extraction is another noteworthy application. In this sector, it functions as a corrosion inhibitor, protecting metal surfaces from oxidation and prolonging the life of extraction equipment. Its incorporation into drilling fluids and acid fracturing fluids helps maintain effective performance, especially in challenging operational environments.
Environmental Considerations
As industries continue to grow increasingly conscious of environmental impacts, the use of ATMP raises questions regarding its biodegradability and ecological effects. While ATMP is considered to have low toxicity to aquatic organisms, there is ongoing research to assess its long-term environmental behavior. The development of bio-based alternatives, alongside improved formulations of ATMP, is a focus within the industry to ensure that water treatment processes remain environmentally sustainable.
Conclusion
Amino tri methylene phosphonic acid is a crucial compound with diverse applications across multiple industries, especially in water treatment and resource management. Its unique structural properties allow it to act as an effective inhibitor of scale formation and a versatile chelating agent capable of enhancing various processes. As research advances, the continued exploration of ATMP's applications and environmental impacts will be paramount in ensuring that it remains a valuable asset in industrial chemistry while promoting sustainable practices.
In summary, ATMP exemplifies the intersection of chemistry and practical application, highlighting the significant role such compounds play in addressing contemporary industrial challenges. As technology evolves, the insights garnered from studying ATMP will undoubtedly lead to further innovations, paving the way for improved efficiency, sustainability, and environmental stewardship in industrial practices.
-
Pbtc Scale InhibitorPBTC: A Scale Protector for Industrial Water TreatmentNewsAug.05,2025
-
Organic Phosphonate: An Efficient Defender in the Field of Scale InhibitionNewsAug.05,2025
-
Hydrolyzed Polymaleic Anhydride: Green Pioneer in Scale Inhibition FieldNewsAug.05,2025
-
PAPEMP Polyamino Polyether Methylene Phosphonic Acid For SaleNewsAug.05,2025
-
Flocculant Water Treatment: A Pioneer in Purification in the Field of Water TreatmentNewsAug.05,2025
-
Benzyl Isothiazolinone: An Efficient and Broad-Spectrum Antibacterial Protective GuardNewsAug.05,2025





