PAC Poly Aluminum Chloride Applications and Benefits in Water Treatment Processes
The Role of PAC (Poly Aluminum Chloride) in Water Treatment
Poly Aluminum Chloride (PAC) has gained significant prominence as a coagulant in water treatment processes. This versatile chemical compound, characterized by its aluminum content and polymeric structure, is widely utilized in municipal and industrial wastewater treatment, as well as in drinking water purification. Its rising popularity can be attributed to several factors, including its effectiveness in forming flocs, its lower dosage requirements compared to traditional coagulants, and its adaptability to varying water qualities.
What is PAC?
PAC is an inorganic polymer that is typically produced by the reaction of aluminum chloride with a base such as sodium hydroxide. This process results in a product that has a higher molecular weight than conventional aluminum salts like aluminum sulfate. This polymeric characteristic allows PAC to more effectively aggregate suspended particles in water, making it an excellent choice for various purification processes.
Advantages of Using PAC
One of the primary benefits of using PAC in water treatment is its ability to operate efficiently across a wide range of pH levels. Traditional coagulants often require specific pH conditions to be effective. In contrast, PAC functions well in both acidic and alkaline conditions, which is essential for treating natural waters that often exhibit fluctuating pH levels. This characteristic makes PAC a more flexible option for water treatment facilities.
Additionally, PAC typically requires a lower dosage compared to aluminum sulfate. This reduced need for coagulant means lower operational costs for facilities, as well as reduced generation of sludge, which is a byproduct of the coagulation process. The smaller volume of sludge is not only cost-effective but also simplifies the treatment and disposal processes.
pac poly aluminum chloride
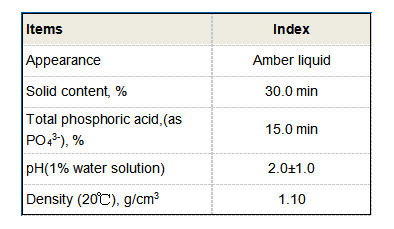
Effectiveness in Different Applications
PAC is highly effective in removing turbidity from water, which is crucial for producing clean, drinkable water. It works by neutralizing the charges on suspended particles, allowing them to clump together and settle at the bottom of the treatment tank. The resultant flocs are much larger and easier to remove than those produced by using traditional coagulants.
Moreover, PAC has been shown to efficiently remove organic matter, color, and other contaminants from water. This makes it particularly valuable in treating water from sources that may contain a variety of pollutants, including industrial effluents. In fact, studies indicate that PAC can significantly improve the quality of water by enhancing removal rates of specific contaminants compared to conventional coagulants.
Environmental Impact
Another important aspect to consider is the environmental impact of using PAC. With a lower dosages resulting in less chemical usage and reduced sludge production, PAC presents an environmentally friendlier option compared to aluminum sulfate. Additionally, the use of PAC can lead to improved effluent quality, which is critical for protecting aquatic ecosystems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Poly Aluminum Chloride stands out as a superior coagulant in the field of water treatment. Its versatility, effectiveness across different water chemistries, and cost-efficiency make it a favorable option for both municipal and industrial applications. As water quality standards continue to rise and the demand for efficient treatment solutions increases, the role of PAC is likely to become even more central in ensuring clean and safe water supplies. As a result, ongoing research and development in the application of PAC could lead to further enhancements in water treatment technologies, paving the way for more sustainable and effective practices in the future.
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





