pbtc scale inhibitorpbtc
The Role of PBTC Scale Inhibitors in Water Treatment
In recent years, the management of water quality has become a critical concern across various industries due to the implications of scale formation. One of the most effective strategies for addressing this issue is the use of PBTC, or phosphonobutyric acid and its derivatives, as scale inhibitors. Understanding the role of PBTC in mitigating scale formation can lead to more efficient water management practices and enhanced operational efficiency in industrial processes.
The Role of PBTC Scale Inhibitors in Water Treatment
PBTC, as a scale inhibitor, works through a mechanism known as threshold reduction. This means that it can effectively prevent the formation of scale at lower concentrations than traditional inhibitors. This property makes PBTC particularly appealing, as it minimizes chemical usage while maximizing efficacy. The phosphonic acid group within PBTC has a strong affinity for calcium and other metal ions, preventing them from precipitating out and forming solid scales.
pbtc scale inhibitorpbtc
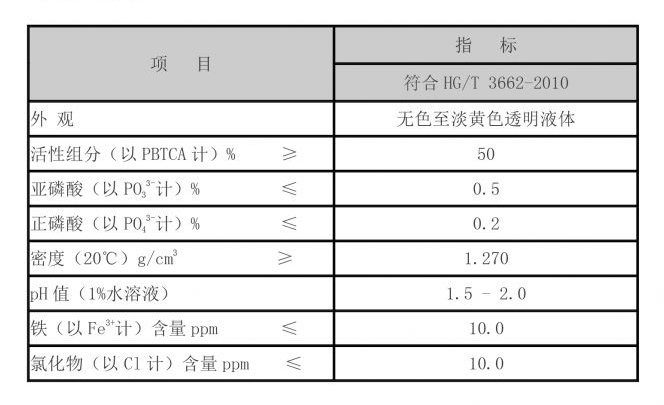
Moreover, PBTC exhibits excellent thermal stability and compatibility with a variety of water chemistries. This versatility allows it to be utilized in different applications ranging from cooling water systems to oil and gas extenders. In cooling towers, for instance, the presence of PBTC can significantly reduce the amount of calcium carbonate and other inorganic salts that typically lead to fouling and scaling. This not only enhances the efficiency of the cooling system but also extends its operational lifespan.
Another significant advantage of using PBTC is its effectiveness at higher temperatures. In many industrial processes, water temperatures can rise significantly, leading to increased risks of scaling. PBTC's stability at elevated temperatures means it can provide continuous protection, ensuring that equipment operates smoothly even under harsh conditions.
In addition to its effectiveness in preventing scale formation, PBTC is also environmentally benign compared to some traditional scale inhibitors. As industries shift towards more sustainable practices, the use of eco-friendly chemicals in water treatment becomes non-negotiable. PBTC's minimal environmental impact makes it an ideal choice in various sectors, including power generation, agriculture, and manufacturing.
In conclusion, the implementation of PBTC as a scale inhibitor presents a multifaceted advantage for industries plagued by scale-related challenges. Its unique properties not only enhance operational efficiency but also promote sustainable practices in water management. As technology continues to evolve, and the need for effective scale management increases, the role of PBTC in water treatment solutions will undoubtedly become more significant. By investing in innovative chemical solutions like PBTC, industries can look forward to improved productivity, reduced costs, and a more sustainable future.
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride: High-Purity DisinfectantNewsAug.30,2025
-
2-Phosphonobutane-1,2,4-Tricarboxylic Acid: Scale & CorrosionNewsAug.29,2025
-
Premium Isothiazolinones | Broad-Spectrum Biocidal SolutionsNewsAug.28,2025
-
LK-319 Special Scale And Corrosion Inhibitor For Steel Plants: Advanced Solutions for Industrial Water SystemsNewsAug.22,2025
-
Flocculant Water Treatment: Essential Chemical Solutions for Purification ProcessesNewsAug.22,2025
-
Isothiazolinones: Versatile Microbial Control Agents for Industrial and Consumer ApplicationsNewsAug.22,2025





