Exploring the Applications and Benefits of Zinc HEDP in Various Industries and Technologies
The Importance of Zinc HEDP in Modern Industries
Zinc Hydroxyethylene Diphosphonate, commonly referred to as Zinc HEDP, has emerged as a critical additive in various industrial applications, particularly in water treatment and corrosion inhibition. As industries prioritize efficiency, sustainability, and cost-effectiveness, the role of Zinc HEDP has grown increasingly vital.
Understanding Zinc HEDP
Zinc HEDP is a phosphonate compound that combines zinc ions with hydroxyethylene diphosphonic acid. This chemical structure provides unique properties that make it particularly useful in water systems. Zinc HEDP is known for its ability to control scale formation, prevent corrosion, and enhance the stability of metal surfaces in aqueous environments.
Applications in Water Treatment
One of the primary applications of Zinc HEDP is in the treatment of water systems. In cooling towers, boilers, and industrial water loops, the presence of minerals and impurities often leads to scale formation and corrosion, which can severely impact operational efficiency and increase maintenance costs. Zinc HEDP acts as an effective scale inhibitor, preventing the deposition of hardness minerals that cause scaling. Additionally, its corrosion-inhibiting properties protect metal surfaces from degradation, ensuring a longer lifespan for equipment and infrastructure.
The use of Zinc HEDP in water treatment is not only effective but is also environmentally friendly. It is biodegradable and does not contribute to the pollution often associated with traditional treatment chemicals. This aligns with the growing emphasis on sustainability within industries, allowing companies to better meet regulatory requirements and consumer expectations.
Benefits Over Traditional Chemicals
zn hedp 锌hedp
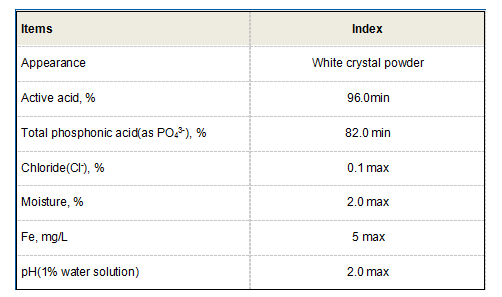
Compared to traditional corrosion inhibitors and scale inhibitors, Zinc HEDP presents several advantages. It is more effective at lower concentrations, reducing the required dosage and overall chemical costs. This efficiency translates into fewer resources consumed and lower impact on the environment. Moreover, Zinc HEDP is compatible with a broad range of other water treatment chemicals, enabling its integration into existing treatment regimens without the risk of adverse reactions.
Another significant benefit of using Zinc HEDP is its ability to function effectively across varying pH levels and temperatures. This versatility makes it suitable for a wide array of applications, from municipal water systems to complex industrial processes.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its numerous advantages, the use of Zinc HEDP is not without challenges. For instance, improper dosing can lead to negative outcomes, including potential toxicity to aquatic life in effluent if discharged in large quantities. Therefore, industries must employ rigorous monitoring and control measures to ensure that Zinc HEDP is used effectively and responsibly.
Additionally, while Zinc HEDP is generally considered safer than many phosphonates, it is essential for companies to stay updated on regulatory guidelines and safety data. As environmental regulations continue to evolve, companies that utilize Zinc HEDP must remain vigilant to avoid non-compliance and potential penalties.
Conclusion
Zinc HEDP represents a significant advancement in the field of water treatment and corrosion inhibition. Its efficient performance, combined with environmental benefits, highlights its potential as a preferred chemical in modern industrial applications. As industries move towards more sustainable practices, the role of Zinc HEDP will likely continue to grow, revolutionizing how companies approach water management and infrastructure maintenance. The future of Zinc HEDP in industrial applications looks bright, promising enhanced operational efficiency and environmental responsibility.
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





