Understanding the Effects of Scale Formation and Corrosion Inhibitors in Industrial Chemical Processes
Understanding Scale and Corrosion Inhibitor Chemicals
Scale and corrosion are two prominent challenges faced in various industries, particularly those involving water systems, such as power generation, oil and gas, and manufacturing. Scale refers to the deposition of minerals — primarily calcium, magnesium, and other compounds — on surfaces in contact with water. Corrosion, on the other hand, is the degradation of materials, usually metals, due to chemical reactions with their environment. Both of these phenomena can lead to significant operational issues, increased maintenance costs, and reduced efficiency. To mitigate these problems, scale and corrosion inhibitor chemicals are employed.
What are Scale Inhibitors?
Scale inhibitors are chemicals that prevent the formation of scale within water systems. They work by either altering the crystallization process of minerals or by dispersing existing scale. The most common types of scale inhibitors include phosphonates, polyacrylates, and thiocarbonates. Phosphonates are particularly effective due to their ability to bind to calcium and other minerals, preventing them from precipitating out of solution and forming hard deposits on equipment surfaces.
In industrial applications, these scale inhibitors are crucial for maintaining the efficiency of heat exchangers, boilers, and cooling towers. Without proper scale control, deposits can act as insulators, reducing heat transfer efficiency and leading to overheating and eventual failure of equipment. Regular use of scale inhibitors can significantly extend the lifespan of machinery and reduce downtime, thereby saving costs in the long run.
Importance of Corrosion Inhibitors
Corrosion inhibitors are chemical compounds designed to reduce the rate of corrosion in metals by forming protective films on their surfaces or by neutralizing corrosive agents in the environment
. There are various types of corrosion inhibitors, including anodic inhibitors, cathodic inhibitors, and mixed inhibitors.scale and corrosion inhibitor chemicals
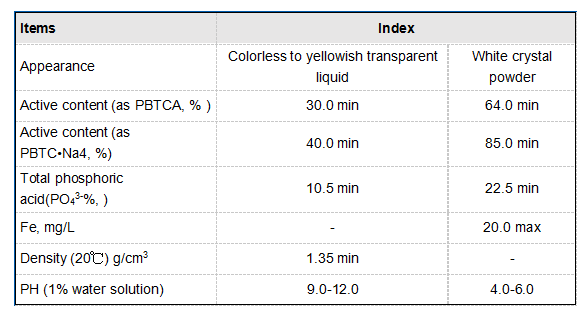
Anodic inhibitors reduce the oxidation of the metal surface, while cathodic inhibitors decrease the reduction reactions. Mixed inhibitors can provide protection against both types of reactions. Common examples include amines, nitrites, and phosphates, which are often used in conjunction with scale inhibitors in water treatment programs.
Using corrosion inhibitors is essential for preventing the deterioration of pipelines, tanks, and other metal structures. In industries where Metal Fatigue and Stress Corrosion Cracking (SCC) can be prevalent, the application of these inhibitors can prevent catastrophic failures that might pose safety risks and financial liabilities.
The Interrelationship Between Scale and Corrosion Inhibition
Scale and corrosion are closely intertwined phenomena; the presence of scale can accelerate corrosion processes by creating localized environments that can retain moisture and corrosive agents. Conversely, corrosion can lead to the release of metal ions into the water, which can contribute to scale formation. Therefore, an integrated approach to water treatment that includes both scale and corrosion inhibition is crucial.
The effectiveness of scale and corrosion inhibitor chemicals depends on various factors, including the concentration of the inhibitors, the pH of the water, temperature, and the presence of other chemicals. Regular monitoring and adjustment of these parameters are essential to ensure optimal protection.
Conclusion
In summary, scale and corrosion inhibitor chemicals play a vital role in the maintenance and efficiency of water systems across various industries. By preventing scale formation and reducing corrosion rates, these chemicals help to ensure the longevity and reliability of equipment, ultimately leading to cost savings and improved operational performance. As industries continue to evolve and face new challenges, the development and application of more effective scale and corrosion inhibition strategies will remain a key focus for engineers and environmental chemists alike.
-
Understanding Polycarboxylic Acids: Properties, Applications, and Future PotentialNewsJul.28,2025
-
Scale Inhibitor Explained: How to Protect Your System from Limescale and Hard Water DamageNewsJul.28,2025
-
Scale and Corrosion Inhibitors: Essential Chemicals for Industrial Water System ProtectionNewsJul.28,2025
-
Polyaspartic Acid: A Biodegradable Polymer for Sustainable ChemistryNewsJul.28,2025
-
Isothiazolinones: A Versatile Antimicrobial Class with Industrial Power and Regulatory ChallengesNewsJul.28,2025
-
A Deep Dive into 2-Phosphonobutane-1,2,4-Tricarboxylic Acid (PBTC)NewsJul.28,2025





