Different Types of Flocculants
Different Types of Flocculants An Overview
Flocculants play a critical role in various industries, particularly in water treatment, mineral processing, and wastewater management. These compounds facilitate the aggregation of fine particles into larger clusters, known as flocs, which can then be easily separated from liquids. Understanding the different types of flocculants is essential for optimizing their use in specific applications.
Natural flocculants are derived from plant or animal sources and are considered environmentally friendly. Common examples include alginates, which are extracted from brown seaweed, and chitosan, obtained from crustacean shells. These biopolymers are effective in diverse applications, particularly in municipal wastewater treatment, where they help in removing suspended solids and organic matter. Their biodegradable nature makes them a sustainable choice, although they may not always provide the same efficiency as synthetic options in industrial applications.
2. Synthetic Organic Flocculants
Synthetic flocculants are widely used due to their high efficiency and ability to be tailored for specific functions. The most common synthetic flocculants are polyacrylamides, which are water-soluble polymers that can enhance sedimentation in various processes. These compounds can be anionic, cationic, or non-ionic, allowing for customization based on the charge characteristics of the particles in the solution. Anionic polyacrylamides are often utilized in wastewater treatment, while cationic versions are employed for dewatering processes in sludge management.
different types of flocculants
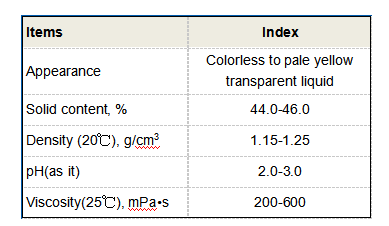
3. Inorganic Flocculants
Inorganic flocculants, such as aluminum sulfate and ferric chloride, are traditional chemical agents used in water treatment. They work by destabilizing colloidal suspensions, allowing for the formation of larger flocs. These flocculants are particularly effective in drinking water treatment processes. They tend to be less expensive than organic options, but they can produce larger amounts of sludge that require further processing and disposal. Inorganic flocculants can also alter the pH of the water, which needs to be monitored closely.
4. Dual-Function Flocculants
Emerging in the industry are dual-function flocculants, which combine the properties of both organic and inorganic flocculants. These hybrid products aim to maximize floc formation while minimizing environmental impact and sludge production. They are becoming increasingly popular as industries seek sustainable solutions without compromising on performance.
In conclusion, the choice of flocculant significantly affects the efficiency of water treatment and related processes. Natural, synthetic, inorganic, and dual-function flocculants each offer unique advantages and applications. As environmental regulations continue to evolve, the development of innovative, sustainable flocculant solutions will remain a focus for researchers and practitioners alike. Understanding these various types is crucial for selecting the right flocculant for specific industrial or municipal needs.
-
lk-319-special-scale-and-corrosion-inhibitor-for-steel-plants-advanced-solutions-for-industrial-water-systemsNewsAug.22,2025
-
flocculant-water-treatment-essential-chemical-solutions-for-purification-processesNewsAug.22,2025
-
isothiazolinones-versatile-microbial-control-agents-for-industrial-and-consumer-applicationsNewsAug.22,2025
-
scale-inhibitor-key-solutions-for-water-system-scale-preventionNewsAug.22,2025
-
organophosphonates-versatile-scale-inhibitors-for-industrial-water-systemsNewsAug.22,2025
-
scale-and-corrosion-inhibitor-essential-chemical-solutions-for-water-system-maintenanceNewsAug.22,2025





