Investigation of pBTC Phosphonate Compounds in Environmental Applications and Impacts
Understanding PBTC Phosphonate A Comprehensive Overview
Phosphonates are an essential class of compounds in multiple applications, particularly within the field of agriculture and water treatment. Among these, PBTC (Potassium Bisphosphonate) has gained traction due to its unique chemical properties and benefits. This article explores the structure, functions, and applications of PBTC phosphonates, shedding light on their significance in various industries.
Chemical Structure and Properties
PBTC belongs to the family of organophosphonates, characterized by the presence of phosphonic acid groups. The phosphorus atom is bonded to four oxygen atoms, some of which can be further modified by alkyl or aryl groups, resulting in various derivatives with distinct properties. The chemical formula of PBTC is often represented as C8H14K2O10P2, highlighting its complexity and potential for diverse interactions.
One of the remarkable aspects of PBTC is its water solubility, which makes it highly effective for use in aqueous systems. The presence of potassium enhances its solubility, allowing for easier application in agricultural and industrial processes. Furthermore, PBTC has chelating properties, enabling it to interact with metal ions, which is advantageous in numerous applications.
Agricultural Applications
In the agricultural sector, PBTC phosphonates play a vital role as fungicides and plant growth enhancers. They have shown efficacy in controlling various plant pathogens, contributing to improved crop yield and quality. The mechanism of action involves the induction of systemic resistance in plants, allowing them to fend off diseases more effectively.
Moreover, PBTC phosphonates are often used in combination with other agrochemicals to enhance their effectiveness. The synergistic effect can lead to reduced application rates, minimizing the environmental impact while maximizing crop protection. This is particularly significant in modern agriculture, where sustainable practices are increasingly required.
Water Treatment
pbtc phosphonate
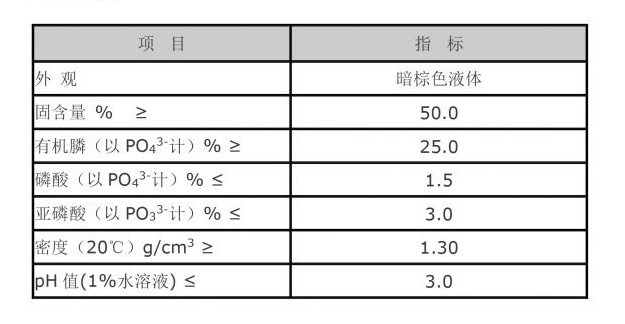
Apart from agriculture, PBTC phosphonates are widely utilized in water treatment facilities. They serve as scale inhibitors, preventing the deposition of mineral salts within pipes, boilers, and cooling systems. This scaling can lead to reduced efficiency and increased maintenance costs, making the application of PBTC crucial for operational integrity.
The chelation properties of PBTC also allow it to sequester metal ions, reducing the potential for water contamination. By binding heavy metals and preventing their precipitation, PBTC contributes to safer water systems, aligning with environmental regulations and health standards.
Industrial Uses
In addition to agricultural and water treatment applications, PBTC phosphonates find roles in various industrial processes. They are employed as additives in detergents, providing enhanced cleaning capabilities by preventing the redeposition of dirt. Their ability to enhance the performance of surfactants can lead to more effective formulations in cleaning products.
PBTC is also used in the production of metal treatments and coatings. Its chelating properties make it useful in stabilizing metal ions, which is crucial in processes such as electroplating, where control over metal deposition is vital for achieving desired surface finishes.
Safety and Environmental Considerations
Like many chemical compounds, the use of PBTC phosphonates necessitates careful consideration of safety and environmental impacts. Regulatory frameworks govern their use, ensuring that they are applied in a manner that minimizes risks to human health and the environment. Research continues to focus on potential toxicity and ecological effects, aiming to demonstrate that PBTC can be used sustainably.
Conclusion
PBTC phosphonates represent a multifaceted class of compounds that provide significant benefits across various sectors. Their unique properties make them indispensable in agriculture, water treatment, and industrial applications. As the demand for sustainable and effective chemical solutions grows, understanding and advancing the use of PBTC phosphonates will be essential. Through ongoing research and development, these compounds stand to play a vital role in addressing modern challenges in farming, water management, and industrial efficiency, paving the way for a more sustainable future.
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





