2 phosphonobutane 1 2 4 tricarboxylic acid
Exploring the Applications of 2% Phosphonobutane-1,2,4-tricarboxylic Acid
Phosphonobutane-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid (PBTC) is a synthetic organic compound that has garnered significant interest in both scientific research and industrial applications. Its unique structure, characterized by three carboxylic acid groups and a phosphonate group, affords it properties that make it a valuable agent in various fields, particularly in water treatment, agriculture, and potentially in pharmaceuticals.
Chemical Structure and Properties
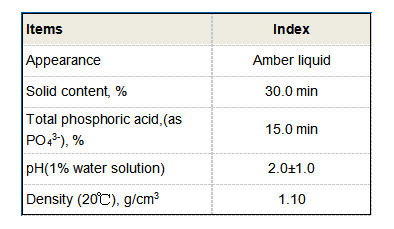
PBTC, also known for its ability to chelate metal ions, possesses a molecular formula of C7H11O9P. The presence of multiple functional groups allows it to interact with a variety of metals, making it an efficient scale inhibitor. This property is particularly useful in industries where water is recirculated in cooling systems and boilers, as scaling can negatively impact equipment efficiency and longevity.
Applications in Water Treatment
One of the most prominent uses of 2% PBTC is in the field of water treatment. The compound is effective in preventing the formation of calcium carbonate and other mineral scales that can accumulate in pipes and machinery. In industrial settings, these scales can lead to reduced heat transfer efficiency, increased energy consumption, and, ultimately, costly shutdowns for maintenance.
PBTC works by chelating calcium and other metal ions in water, thus inhibiting their ability to precipitate and form hard scale deposits. Its effectiveness at relatively low concentrations, like the 2% solution, makes it both an economical and environmentally beneficial choice compared to traditional phosphates.
Role in Agriculture
Beyond its applications in industrial water management, PBTC has shown promise in agricultural contexts. The compound can enhance the availability of essential nutrients, particularly micronutrients, within the soil. Its chelating properties can help maintain nutrient solubility, which improves nutrient uptake by plants. Furthermore, PBTC can assist in optimizing soil pH and improving overall soil health, contributing to enhanced crop yields.
2 phosphonobutane 1 2 4 tricarboxylic acid
In fertigation practices—where fertilizers are applied directly through irrigation systems—PBTC can be included to maximize fertilizer efficiency. Its ability to bind nutrients ensures they remain available to the root systems of plants, reducing waste and enhancing growth.
Potential in Pharmaceuticals
As research into the pharmacological applications of various chelating agents expands, PBTC is being investigated for its potential roles in pharmaceuticals. The unique ability of PBTC to form stable complexes with metal ions could be beneficial for drug delivery systems, particularly for drugs that require metal ion stabilization.
Additionally, the phosphonate group in its structure may provide anti-cancer properties, as phosphonates have shown potential in inhibiting tumor growth in preliminary studies. While much work remains to be done to explore and confirm these possibilities, the initial findings suggest that PBTC might have a place in the future of medical therapeutics.
Environmental Considerations
The increasing scrutiny of chemical usage in industry and agriculture has led to a demand for environmentally friendly alternatives. PBTC stands out as a biodegradable chelating agent that poses lesser risks to aquatic environments compared to traditional phosphates. Its use in water treatment aligns with global sustainability goals and reflects a shift towards greener chemistry.
Conclusion
In summary, the 2% solution of phosphonobutane-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid is a versatile compound with diverse applications ranging from industrial water treatment to agricultural innovation and potential pharmaceutical use. Its chelating properties and environmental advantages position PBTC as a valuable asset in various sectors. Continued research and development will likely unveil even more applications, reinforcing the importance of this compound in contributing to efficiency and sustainability in both industrial and agricultural settings. As reliance on innovative chemical solutions grows, so too will the relevance of compounds like PBTC in shaping a more sustainable future.
-
Pbtc Scale InhibitorPBTC: A Scale Protector for Industrial Water TreatmentNewsAug.05,2025
-
Organic Phosphonate: An Efficient Defender in the Field of Scale InhibitionNewsAug.05,2025
-
Hydrolyzed Polymaleic Anhydride: Green Pioneer in Scale Inhibition FieldNewsAug.05,2025
-
PAPEMP Polyamino Polyether Methylene Phosphonic Acid For SaleNewsAug.05,2025
-
Flocculant Water Treatment: A Pioneer in Purification in the Field of Water TreatmentNewsAug.05,2025
-
Benzyl Isothiazolinone: An Efficient and Broad-Spectrum Antibacterial Protective GuardNewsAug.05,2025





