poly aluminum chloride
Poly Aluminum Chloride A Comprehensive Overview
Poly Aluminum Chloride (PAC) is an inorganic polymer widely utilized in various industries, predominantly in water treatment processes. As a versatile coagulant, PAC has gained prominence due to its effectiveness in purifying water and its ability to remove impurities, including suspended solids, organic matter, and heavy metals. The increasing demand for clean water and stringent regulations regarding wastewater management have further propelled the use of PAC in recent years.
Composition and Properties
PAC is produced by the hydrolysis of aluminum chloride, resulting in a compound with a wide range of molecular weights and characteristics. The chemical formula of PAC can be represented as Aln(OH)mCl(3n-m), where n signifies the degree of polymerization, and m indicates the number of hydroxyl groups. This structure allows PAC to bridge particles and facilitate their aggregation, leading to effective flocculation and sedimentation.
One of the remarkable properties of PAC is its high performance at low doses compared to traditional coagulants like aluminum sulfate. The optimal pH range for PAC is between 6.0 and 8.0, making it suitable for a wide range of water conditions. Additionally, PAC has a lower residual aluminum content in treated water, which is a significant advantage considering the health concerns associated with aluminum exposure.
Applications in Water Treatment
In the realm of water treatment, PAC serves multiple functions. Its primary application lies in drinking water purification, where it helps eliminate turbidity and enhance clarity. It is also employed in industrial wastewater treatment, where it effectively removes contaminants and meets regulatory discharge standards. The use of PAC extends to municipal water supply systems, paper production, textile manufacturing, and even in oil drilling operations, highlighting its versatility.
One significant advantage of using PAC in water treatment is its ability to operate effectively across varying water conditions. It can efficiently coagulate and flocculate particles in both acidic and alkaline waters, adapting to the specific requirements of each treatment scenario. The resulting flocs formed during the PAC treatment process are generally denser and settle faster, accelerating sedimentation and improving overall treatment efficiency.
poly aluminum chloride
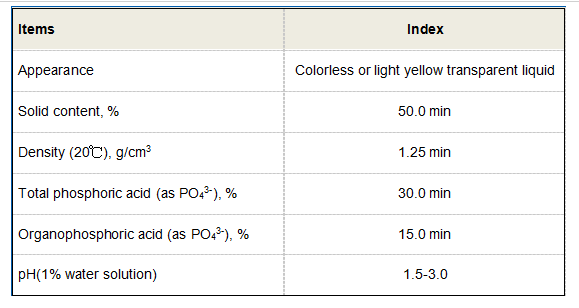
Advantages Over Traditional Coagulants
The advantages of PAC over traditional coagulants such as aluminum sulfate or ferric chloride are numerous. First, PAC’s lower dosage requirements lead to cost savings, as users can achieve similar or superior results with smaller amounts of chemical. Second, its reduced sludge production minimizes disposal issues and associated costs. The enhanced performance in a broader pH range allows for greater flexibility in treatment processes.
Moreover, PAC exhibits less sensitivity to water temperature compared to other coagulants. This characteristic is particularly beneficial in regions with seasonal temperature fluctuations, ensuring consistent treatment effectiveness throughout the year.
Environmental Considerations
While PAC presents numerous benefits, it is essential to consider its environmental implications. The production and application of PAC should align with sustainable practices to minimize any potential adverse effects. Regulatory bodies often monitor the usage of coagulants, including PAC, to ensure that water treatment processes do not compromise aquatic ecosystems.
Furthermore, ongoing research into the biodegradability and toxicity of PAC is vital to establishing its long-term environmental impact. By adhering to safety regulations and best practices, the industry can leverage the advantages of PAC while maintaining ecological balance.
Conclusion
In summary, Poly Aluminum Chloride is a pivotal player in the field of water treatment, offering an effective solution for purifying water and meeting environmental standards. Its favorable properties, combined with its applicability across various industries, make PAC a preferred choice for many water treatment professionals. As the demand for clean water continues to rise, the role of PAC is likely to expand, supporting sustainable practices in water management.
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





