Investigation of Polydisperse HEDP Effects on Chemical Performance and Stability
Exploring the Characteristics and Applications of Polydisperse HEDP (Hydroxyethylidene Diphosphonic Acid)
Polydisperse HEDP, or Hydroxyethylidene Diphosphonic Acid, is a phosphonic acid commonly used in various industrial applications due to its remarkable chelating properties. With a unique ability to bind metal ions, HEDP finds its utilization in water treatment, scale inhibition, and corrosion prevention. The term polydisperse refers to the distribution of molecular sizes within a sample, which can significantly influence the performance and effectiveness of HEDP in different contexts.
Understanding Polydispersity in HEDP
Polydispersity denotes the existence of molecules of varying sizes and weights within a polymer or oligomer sample. In the case of polydisperse HEDP, this variability can affect its solubility, binding efficiency, and stability in solution. The molecular size distribution contributes to the effectiveness of HEDP in chelation, as different metal ions may interact differently with the different molecular species present in a polydisperse sample.
The polydispersity index (PDI) quantifies this distribution and is a critical parameter in evaluating the performance of HEDP in various applications. A lower PDI indicates a uniform molecule size, which is often preferable in certain applications. However, a polydisperse system can provide a broader range of interaction sites, enhancing the versatility and overall performance of HEDP in real-world scenarios.
Applications of HEDP in Industry
1. Water Treatment HEDP is widely employed in the treatment of industrial water systems. Its ability to form stable complexes with calcium, magnesium, and other metal ions helps prevent the formation of scale deposits in pipes and boilers. By controlling scale formation, HEDP contributes to the efficiency and longevity of industrial equipment.
2. Corrosion Inhibition HEDP also serves as a corrosion inhibitor in various aqueous environments. The chelation of metal ions prevents the oxidation processes that contribute to corrosion, thus protecting metal surfaces in cooling systems, heating systems, and other equipment exposed to water.
polydisperse hedp
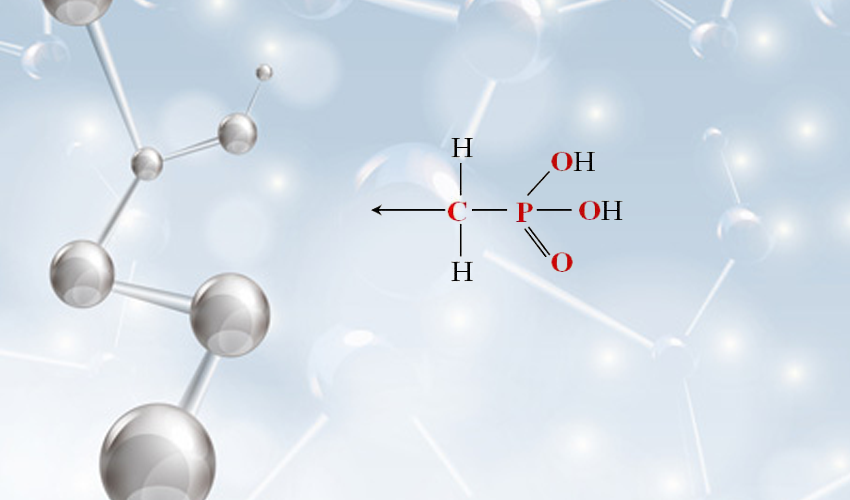
3. Detergency In other applications, particularly in household and industrial detergents, HEDP’s chelating properties help soften water by binding hardness ions, increasing the effectiveness of surfactants and improving cleaning performance.
4. Agricultural Sector HEDP has found its way into agriculture, where it is used as a component in fertilizers. By chelating micronutrients, HEDP aids in enhancing nutrient uptake in plants, leading to improved growth and yield.
5. Oil and Gas Industry In the oil and gas sector, HEDP is used to control scale formation in various processes, thus ensuring that extraction and refinement operations run smoothly without interruptions due to equipment fouling or failure.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite its many advantages, the use of polydisperse HEDP can present challenges. The variability in molecular size may lead to inconsistent performance in some applications. Continuous research is essential to optimize the synthesis of HEDP to achieve desired molecular characteristics that suit specific needs.
Moreover, environmental concerns surrounding phosphonate compounds like HEDP have led to stringent regulatory scrutiny. Thus, the development of more environmentally friendly alternatives, or modifications to HEDP that reduce ecological impact while maintaining effectiveness, is a critical area of ongoing research.
Conclusion
Polydisperse HEDP is a versatile compound with significant industrial applications ranging from water treatment to agriculture and the oil industry. Its unique properties stem from its polydisperse nature, which contributes to its effectiveness in binding metal ions and preventing scale formation. As industries continue to seek sustainable solutions, the role of HEDP will evolve, necessitating further innovation and adaptation. Understanding the characteristics and applications of polydisperse HEDP is vital for leveraging its benefits while addressing the challenges it poses in various industrial settings.
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





