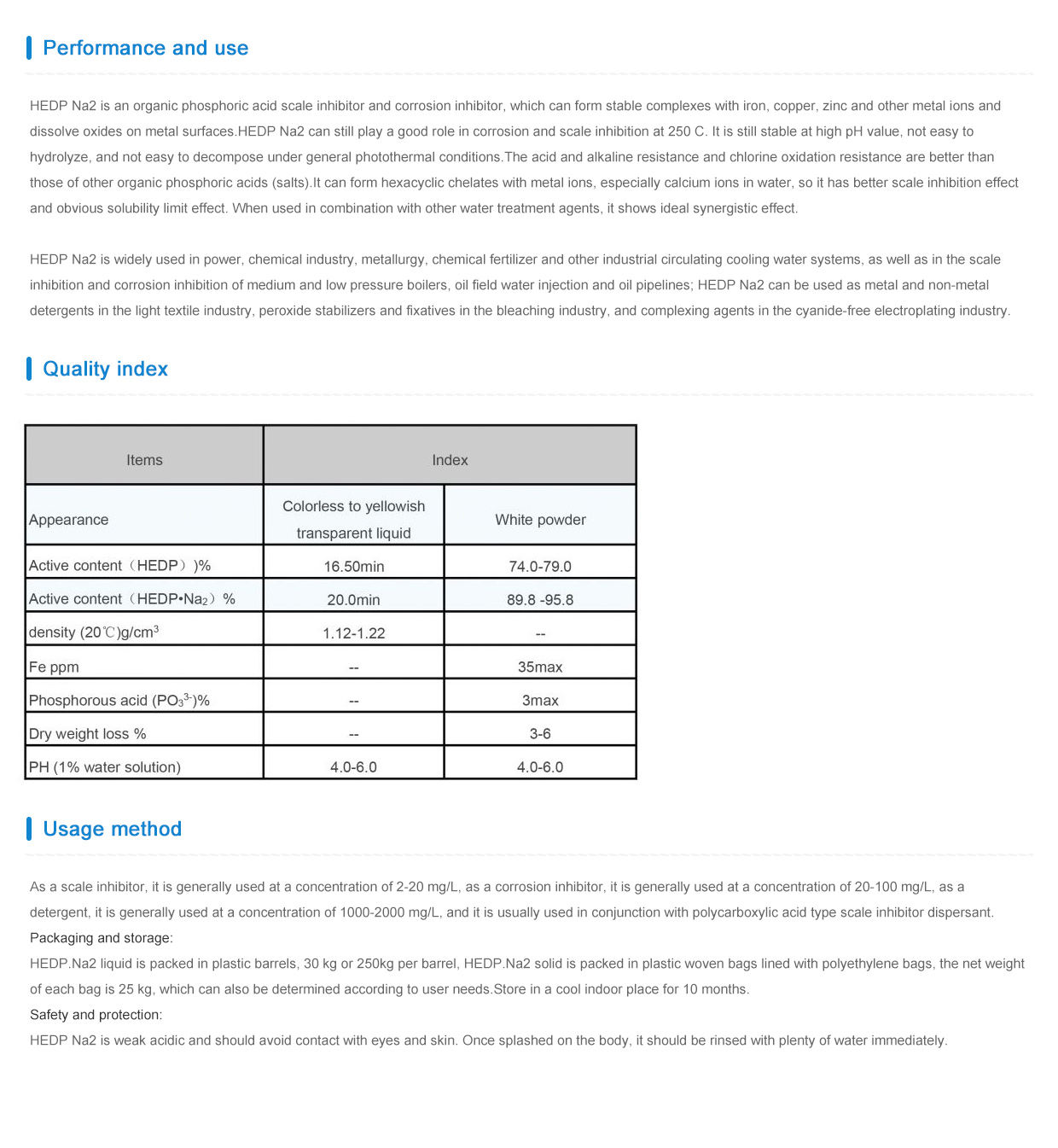
Differences Between Flocculants and Coagulants in Water Treatment Processes
Understanding Flocculants vs. Coagulants Key Differences and Applications
In the field of water treatment and wastewater management, the terms flocculant and coagulant are often used interchangeably, yet they refer to distinct processes and chemicals. Understanding the differences between these two agents is crucial for optimizing water treatment processes, improving efficiency, and achieving desired water quality standards.
Coagulants The First Step in Water Treatment
Coagulants are chemical substances that facilitate the aggregation of small particles into larger clusters, known as flocs. This process is called coagulation and is an essential initial step in the treatment of drinking water and wastewater. Coagulants function by neutralizing the electric charges that keep fine particles suspended in water. Common coagulants include alum (aluminum sulfate), ferric chloride, and polyaluminum chloride (PAC).
When coagulants are added to water, they form a gelatinous precipitate that attracts and binds with suspended solids and colloids, allowing them to clump together. This process significantly enhances the removal of contaminants such as silt, organic matter, and microbes. The resulting flocs can then be removed from the water through sedimentation or filtration.
Flocculants Enhancing the Coagulation Process
While coagulants initiate the aggregation process, flocculants play a critical role in enhancing the process. Flocculants are typically long-chain polymers that promote the growth of larger flocs by further bridging smaller particles that have already been agglomerated by coagulants. By improving particle density and size, flocculants facilitate quicker sedimentation and more efficient removal of particles from water.
These agents are particularly effective in various applications, including industrial wastewater treatment, mining operations, and clarifying drinking water. Common flocculants include polyacrylamides, cationic and anionic polymers, which are chosen based on the specific characteristics of the water being treated.
flocculant vs coagulant
Key Differences Between Coagulants and Flocculants
The primary distinction between coagulants and flocculants lies in their chemical structure and the role they play in water treatment. Coagulants are typically inorganic salts that destabilize particles in suspension through charge neutralization. In contrast, flocculants are organic polymers designed to enhance the formation and growth of flocs resulting from coagulation.
Another significant difference is the timing and dosage of application. Coagulants are added in the initial stages of the treatment process, whereas flocculants are added subsequently to optimize floc growth and improve the efficiency of solid-liquid separation.
Selecting the Right Agent for Treatment
Choosing between coagulants and flocculants depends on multiple factors, including the water quality, the nature of the contaminants, and the treatment objectives. While coagulants are effective for reducing turbidity and removing suspended solids, flocculants are indispensable for polishing water after the coagulation phase, ensuring maximum clarity and purity.
Additionally, environmental considerations such as the potential for residual chemicals in treated water influence the selection process. Utilizing the appropriate combination of coagulants and flocculants can optimize treatment efficiency, reduce chemical usage, and enhance the overall effectiveness of the purification process.
Conclusion
In summary, both coagulants and flocculants are essential components of modern water treatment practices. While they serve distinctive roles, understanding their differences and how they work together is vital for achieving optimal results in the purification of water and wastewater. By leveraging the strengths of both agents, water treatment facilities can ensure cleaner, safer water for communities and ecosystems alike.
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





