Understanding the Properties and Applications of Hydrolyzed Polyacrylamide in Industry
Hydrolyzed Polyacrylamide An Overview of Its Properties and Applications
Hydrolyzed polyacrylamide (HPAM) is a versatile polymer that has gained considerable attention in various industries due to its unique properties and functionalities. As a water-soluble polymer, HPAM is a derivative of polyacrylamide, which undergoes hydrolysis to introduce functional groups that enhance its performance in different applications. This article will explore the characteristics, production methods, and diverse applications of hydrolyzed polyacrylamide, highlighting its significance across various fields.
Properties of Hydrolyzed Polyacrylamide
One of the primary characteristics of hydrolyzed polyacrylamide is its high viscosity in aqueous solutions. This property makes HPAM an excellent thickening agent, particularly in formulations where maintaining a consistent texture is essential. The degree of hydrolysis can significantly affect the properties of HPAM, including its molecular weight and solubility, allowing for tailored applications across industries. Additionally, HPAM exhibits excellent flocculating properties, enabling it to effectively aggregate solid particles dispersed in liquids.
Another notable property is its ability to form gels or hydrogels, particularly when cross-linked with other agents. These gels are beneficial for applications that require controlled release of active ingredients or moisture retention, making them valuable in agricultural and cosmetic formulations. Moreover, due to its non-toxic nature, HPAM is considered safe for various uses, making it an attractive option in consumer products.
Production Methods
Hydrolyzed polyacrylamide is produced through a hydrolysis process that involves the reaction of polyacrylamide with water, often in the presence of a catalyst. The extent of hydrolysis can be controlled by adjusting reaction conditions such as temperature, pressure, and reaction time. This control allows manufacturers to create HPAM with specific molecular weights and degrees of hydrolysis tailored for intended applications.
To ensure product quality, various analytical techniques, including gel permeation chromatography (GPC) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, are employed to characterize the resulting polymers. These methods help in determining the degree of hydrolysis, molecular weight, and purity, crucial factors that influence the performance of HPAM in its applications.
Applications of Hydrolyzed Polyacrylamide
hydrolyzed polyacrylamide
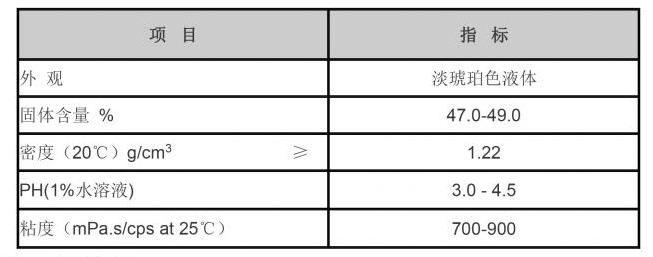
Hydrolyzed polyacrylamide finds applications in numerous sectors, including
1. Oil and Gas Industry HPAM is widely used as a water control agent and a viscosity enhancer in enhanced oil recovery (EOR) processes. Its ability to improve the mobility of oil and reduce water permeability in reservoir rocks makes it essential for maximizing oil extraction efficiency.
2. Environmental Remediation The flocculating properties of HPAM make it a valuable agent for water treatment processes. It helps in the removal of suspended solids and heavy metals from wastewater, contributing to cleaner water bodies and improved environmental health.
3. Agriculture In agricultural settings, HPAM is used as a soil conditioner and water-retaining agent. By enhancing soil structure and moisture retention, it supports plant growth and helps in drought management.
4. Cosmetics and Personal Care HPAM acts as a thickener and stabilizer in cosmetic formulations such as lotions, creams, and gels, providing desirable textures and enhancing the efficacy of active ingredients.
5. Construction In construction, HPAM is utilized as a rheology modifier in cement-based formulations. It helps improve the workability and stability of cement mixtures, leading to enhanced performance and durability of construction materials.
Conclusion
Hydrolyzed polyacrylamide is a multifunctional polymer with significant potential across diverse industries. Its unique properties, coupled with the ability to tailor its characteristics through controlled hydrolysis, make it an invaluable resource in oil recovery, water treatment, agriculture, cosmetics, and construction. As research continues to unveil new applications and enhance its properties, HPAM is poised to play an increasingly important role in addressing various industrial challenges.
-
Understanding Polycarboxylic Acids: Properties, Applications, and Future PotentialNewsJul.28,2025
-
Scale Inhibitor Explained: How to Protect Your System from Limescale and Hard Water DamageNewsJul.28,2025
-
Scale and Corrosion Inhibitors: Essential Chemicals for Industrial Water System ProtectionNewsJul.28,2025
-
Polyaspartic Acid: A Biodegradable Polymer for Sustainable ChemistryNewsJul.28,2025
-
Isothiazolinones: A Versatile Antimicrobial Class with Industrial Power and Regulatory ChallengesNewsJul.28,2025
-
A Deep Dive into 2-Phosphonobutane-1,2,4-Tricarboxylic Acid (PBTC)NewsJul.28,2025





