Jun . 14, 2024 14:14
Back to list
Triethylene glycol penta-, a chemical compound
Understanding Diethylenetriamine (DETA) and its Penta- Derivatives
Diethylenetriamine (DETA), a colorless, hygroscopic liquid with a characteristic ammonia-like odor, is an organic compound of significant importance in various industrial applications. The chemical formula for DETA is C6H14N2, indicating its structure as a diamine with two primary amine groups and one secondary amine group. This versatile compound plays a crucial role in the synthesis of polymers, corrosion inhibitors, and as a catalyst in chemical reactions.
DETA's penta- derivatives, often referred to as DETA-pentas, are formed when DETA reacts with other compounds, particularly with acids or aldehydes, creating a series of complex molecules. These derivatives have a wide range of properties and uses, depending on the specific compound they form. They can be used as chelating agents, which are capable of binding metal ions, making them invaluable in fields such as water treatment, where they help remove heavy metals from water sources.
One of the most well-known DETA-pentas is the ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), a widely used chelating agent. EDTA forms strong complexes with metal ions, making it ideal for applications like removing scale from water pipes, stabilizing food colors, and even in medical procedures to remove heavy metal poisoning.
In the realm of polymer chemistry, DETA-pentas find use as cross-linking agents, enhancing the mechanical strength and stability of polymers. Their ability to form multiple bonds with other molecules makes them valuable in the production of high-performance materials, such as heat-resistant resins and elastomers.
Furthermore, DETA and its derivatives have been explored in the field of biochemistry and pharmaceuticals
Furthermore, DETA and its derivatives have been explored in the field of biochemistry and pharmaceuticals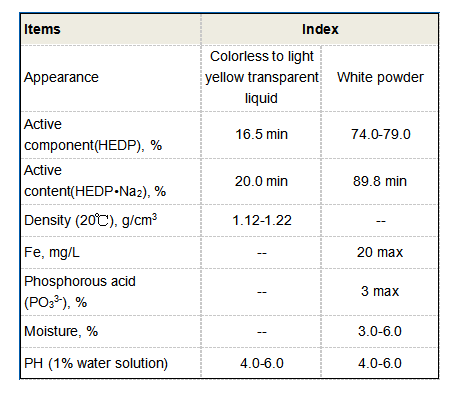 Furthermore, DETA and its derivatives have been explored in the field of biochemistry and pharmaceuticals
Furthermore, DETA and its derivatives have been explored in the field of biochemistry and pharmaceuticals
Furthermore, DETA and its derivatives have been explored in the field of biochemistry and pharmaceuticals
Furthermore, DETA and its derivatives have been explored in the field of biochemistry and pharmaceuticals diethylenetriamine penta . Researchers have investigated their potential in drug delivery systems due to their capacity to interact with biological molecules. Some DETA-based compounds have shown promise as antioxidants, protecting cells from oxidative stress, and as potential treatments for neurodegenerative diseases.
Despite its numerous benefits, the use of DETA and its derivatives also raises environmental concerns. Their potential to leach into water systems and accumulate in ecosystems necessitates careful handling and disposal practices. Researchers continue to work on developing more eco-friendly alternatives while maintaining the desired chemical properties.
In conclusion, diethylenetriamine and its penta- derivatives are multifaceted compounds with a broad spectrum of applications across industries. From water treatment to pharmaceutical development, their unique chemical structures enable them to play critical roles in modern technology. However, it is essential to balance their utility with environmental responsibility, ensuring sustainable use and minimizing potential harm. As scientific knowledge advances, so does our understanding and utilization of these remarkable compounds.
diethylenetriamine penta . Researchers have investigated their potential in drug delivery systems due to their capacity to interact with biological molecules. Some DETA-based compounds have shown promise as antioxidants, protecting cells from oxidative stress, and as potential treatments for neurodegenerative diseases.
Despite its numerous benefits, the use of DETA and its derivatives also raises environmental concerns. Their potential to leach into water systems and accumulate in ecosystems necessitates careful handling and disposal practices. Researchers continue to work on developing more eco-friendly alternatives while maintaining the desired chemical properties.
In conclusion, diethylenetriamine and its penta- derivatives are multifaceted compounds with a broad spectrum of applications across industries. From water treatment to pharmaceutical development, their unique chemical structures enable them to play critical roles in modern technology. However, it is essential to balance their utility with environmental responsibility, ensuring sustainable use and minimizing potential harm. As scientific knowledge advances, so does our understanding and utilization of these remarkable compounds.
 Furthermore, DETA and its derivatives have been explored in the field of biochemistry and pharmaceuticals
Furthermore, DETA and its derivatives have been explored in the field of biochemistry and pharmaceuticals
Furthermore, DETA and its derivatives have been explored in the field of biochemistry and pharmaceuticals
Furthermore, DETA and its derivatives have been explored in the field of biochemistry and pharmaceuticals diethylenetriamine penta . Researchers have investigated their potential in drug delivery systems due to their capacity to interact with biological molecules. Some DETA-based compounds have shown promise as antioxidants, protecting cells from oxidative stress, and as potential treatments for neurodegenerative diseases.
Despite its numerous benefits, the use of DETA and its derivatives also raises environmental concerns. Their potential to leach into water systems and accumulate in ecosystems necessitates careful handling and disposal practices. Researchers continue to work on developing more eco-friendly alternatives while maintaining the desired chemical properties.
In conclusion, diethylenetriamine and its penta- derivatives are multifaceted compounds with a broad spectrum of applications across industries. From water treatment to pharmaceutical development, their unique chemical structures enable them to play critical roles in modern technology. However, it is essential to balance their utility with environmental responsibility, ensuring sustainable use and minimizing potential harm. As scientific knowledge advances, so does our understanding and utilization of these remarkable compounds.
diethylenetriamine penta . Researchers have investigated their potential in drug delivery systems due to their capacity to interact with biological molecules. Some DETA-based compounds have shown promise as antioxidants, protecting cells from oxidative stress, and as potential treatments for neurodegenerative diseases.
Despite its numerous benefits, the use of DETA and its derivatives also raises environmental concerns. Their potential to leach into water systems and accumulate in ecosystems necessitates careful handling and disposal practices. Researchers continue to work on developing more eco-friendly alternatives while maintaining the desired chemical properties.
In conclusion, diethylenetriamine and its penta- derivatives are multifaceted compounds with a broad spectrum of applications across industries. From water treatment to pharmaceutical development, their unique chemical structures enable them to play critical roles in modern technology. However, it is essential to balance their utility with environmental responsibility, ensuring sustainable use and minimizing potential harm. As scientific knowledge advances, so does our understanding and utilization of these remarkable compounds. Share
Latest news
-
Pbtc Scale InhibitorPBTC: A Scale Protector for Industrial Water TreatmentNewsAug.05,2025
-
Organic Phosphonate: An Efficient Defender in the Field of Scale InhibitionNewsAug.05,2025
-
Hydrolyzed Polymaleic Anhydride: Green Pioneer in Scale Inhibition FieldNewsAug.05,2025
-
PAPEMP Polyamino Polyether Methylene Phosphonic Acid For SaleNewsAug.05,2025
-
Flocculant Water Treatment: A Pioneer in Purification in the Field of Water TreatmentNewsAug.05,2025
-
Benzyl Isothiazolinone: An Efficient and Broad-Spectrum Antibacterial Protective GuardNewsAug.05,2025





