polyacrylamide formation
The Formation of Polyacrylamide A Versatile Polymer
Polyacrylamide, a synthetic polymer derived from acrylamide monomers, has gained significant attention in various fields due to its unique properties and applications. Its formation involves a simple yet effective polymerization process that allows for the creation of a versatile material used in numerous industries. This article explores the formation of polyacrylamide, its characteristics, and its diverse applications.
The Polymerization Process
The formation of polyacrylamide typically begins with the polymerization of acrylamide, a white crystalline solid that is soluble in water. The process can occur through two primary methods free radical polymerization and ionic polymerization.
In free radical polymerization, initiators such as ammonium persulfate or azobisisobutyronitrile are used to generate free radicals under suitable conditions (typically heat). These free radicals react with acrylamide monomers to start a chain reaction, leading to the formation of long polymer chains. The reaction can be controlled through temperature, concentration, and the presence of various additives, allowing for the manipulation of the polymer’s molecular weight and structure.
Ionic polymerization, on the other hand, employs anionic or cationic initiators and is characterized by faster polymer growth and the potential for more uniform molecular weights. This method is often used when specific characteristics of the polymer, such as reactivity or solubility, are required.
After polymerization, the resulting polyacrylamide can either be produced as a linear polymer or as a cross-linked polymer, depending on the intended application. Cross-linking creates a three-dimensional network structure, greatly enhancing the polymer’s strength and dimensional stability.
Properties of Polyacrylamide
Polyacrylamide possesses several desirable properties that make it suitable for various applications. One of its most significant attributes is its excellent water absorption capacity. This characteristic is particularly valuable in agriculture and environmental management, where polyacrylamide is used to improve soil moisture retention and manage water resources more effectively.
polyacrylamide formation
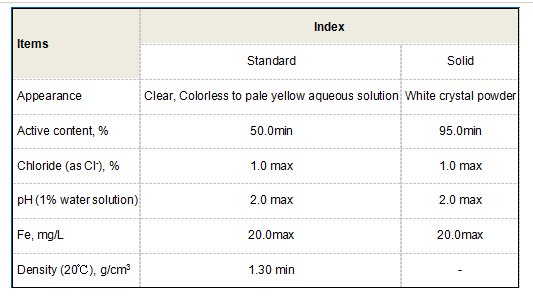
Additionally, polyacrylamide exhibits good chemical stability and can resist degradation in various environmental conditions. Its ability to form gels, coatings, and films makes it a popular choice in laboratories and industrial applications. Furthermore, the polymer can be modified chemically to enhance specific properties, such as hydrophilicity or ionic charge, broadening the scope of its applications.
Applications of Polyacrylamide
The versatility of polyacrylamide leads to its utilization in multiple sectors. In the field of water treatment, polyacrylamide plays a critical role as a flocculant. It aids in the aggregation of suspended particles, facilitating their removal from wastewater and improving overall water quality.
In agriculture, polyacrylamide is employed to reduce soil erosion, enhance water retention in soil, and optimize the use of fertilizers. Its application in soil amendments contributes to sustainable farming practices, promoting efficient water usage and higher crop yields.
Furthermore, polyacrylamide serves as a crucial component in the medical and pharmaceutical industries. It is used in drug delivery systems, tissue engineering, and as a stabilizing agent in various formulations due to its biocompatibility.
In the cosmetics industry, polyacrylamide is found in skin creams and makeup products for its thickening and emulsifying properties. Its ability to form films also contributes to water-resistant formulations.
Conclusion
The formation of polyacrylamide through polymerization is a fundamental process that leads to a polymer with remarkable versatility and applicability. From enhancing agricultural practices to improving water treatment processes and supporting advancements in medical technology, polyacrylamide's diverse range of uses highlights its significance in modern science and industry. As research continues to advance, the potential applications of polyacrylamide will likely expand, solidifying its role as an essential material in various fields.
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





