butane 1 2 4 tricarboxylic acid
The Role of Butane-1,2,4-Tricarboxylic Acid in Modern Chemistry
Butane-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid, often encountered in scientific literature as a unique and versatile compound, plays a vital role in various fields of chemistry. This tricarboxylic acid is structurally characterized by three carboxylic acid (-COOH) groups attached to a butane backbone. This structural feature imparts significant chemical properties that make it valuable in organic synthesis, materials science, and biochemistry.
Chemical Properties and Synthesis
The synthesis of butane-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid typically involves multi-step organic reactions. One of the common methods includes the oxidation of butanoic acids and subsequent reactions to introduce additional carboxylic groups into the molecule. The compound exhibits both acidity and reactivity, which are attributable to the presence of multiple carboxylic acid functional groups. These groups enable butane-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid to undergo a wide range of chemical reactions, including esterification, amidation, and decarboxylation.
The acidity of the carboxylic groups allows this compound to act as a buffering agent in various chemical reactions. Its pKa values suggest that it is significantly acidic, making it an efficient proton donor. This property has implications in organic chemistry, particularly in reaction mechanisms that involve proton transfer.
Applications in Organic Synthesis
In organic synthesis, butane-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid serves as a versatile building block. Its functional groups can be modified to create a variety of derivatives that are important in synthesizing more complex organic molecules. For instance, by reacting with alcohols, it can form esters, which are essential in the production of biodegradable plastics and other materials. Furthermore, it can react with amines to form amides, expanding its utility in pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals.
Moreover, this compound has been utilized in the preparation of polycarboxylic acids, which are essential components in the production of detergents, surfactants, and various polymeric materials. The multifunctionality of butane-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid makes it an attractive candidate for developing innovative materials with specific properties tailored for application in diverse industries.
butane 1 2 4 tricarboxylic acid
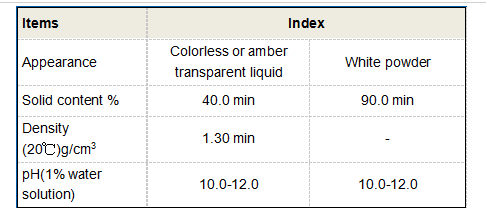
Role in Biochemistry
The significance of butane-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid extends into the realm of biochemistry as well. Its structural similarities to other critical biochemical compounds enable it to play a role in metabolic pathways. For example, tricarboxylic acids are central to the Krebs cycle, which is fundamental to cellular respiration and energy production. While butane-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid is not a direct participant in the Krebs cycle, studying its analogs and derivatives aids in understanding metabolic processes.
Research has indicated that compounds similar to butane-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid can interact with various enzymes, potentially influencing metabolic pathways and serving as inhibitors or activators. This has implications for drug discovery and development, particularly in targeting specific metabolic dysfunctions.
Environmental and Industrial Impact
The environmental impact of chemical compounds is an increasingly important aspect of modern chemistry. Butane-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid, due to its biodegradable nature, is being explored as a substitute for more harmful synthetic compounds in industrial applications. Its potential to break down into less toxic components suggests that it can be integrated into more sustainable production processes.
For instance, research into its application in creating bio-based polymers is gaining momentum. These polymers, derived from renewable resources, could diminish reliance on petroleum-based plastics, addressing ecological concerns related to plastic waste.
Conclusion
In conclusion, butane-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid is a remarkable compound with a diverse range of applications across various fields in chemistry. From organic synthesis to biochemistry and environmental science, its versatility and unique properties make it a subject of continued research and exploration. As the demand for sustainable and efficient chemical solutions rises, compounds like butane-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid will undoubtedly play a crucial role in shaping the future of modern chemistry, promoting innovation and sustainability in both industrial and scientific domains.
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





