Feb . 02, 2025 04:21
Back to list
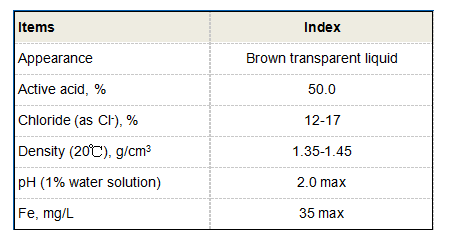
2-Phosphonobutane -1,2,4-Tricarboxylic Acid(PBTC)
In the realm of water treatment and industrial processing, the terms flocculant and coagulant often emerge as pivotal agents. Despite their intertwined applications, they perform distinct yet complementary roles predicated on their unique characteristics and functionalities, crucial for optimizing various processes.
In industrial applications, the selection of specific coagulants and flocculants extends beyond the fundamental chemistry. Considerations include water composition, process economics, regulatory impact, and downstream effects. Industries, from wastewater treatment to mining and food processing, leverage this understanding to improve operational efficiency and regulatory compliance. For instance, a paper mill might select flocculants based on their ability to enhance fiber recovery while minimizing sludge production. Trustworthiness in the choice and application of these chemicals is bolstered by collaborating with reputable suppliers who provide robust technical support and thorough product testing. This ensures the chosen solutions not only meet but exceed industry standards and environmental regulations. This nuanced approach translates into significant economic benefits by reducing chemical consumption, minimizing waste production, and optimizing the overall water or process treatment efficiency. Within industries, adopting tailored solutions tailored to specific water chemistry and operational demands results in reduced operational costs, improved sustainability profiles, and enhanced product quality. Additionally, continual advancements in polymer chemistry and process engineering unlock new potentials for both coagulants and flocculants. Innovations such as biodegradable flocculants or enhanced coagulant formulations with lower toxicity profiles align with the increasing environmental consciousness among industries and consumers alike. In conclusion, distinguishing between flocculants and coagulants is not solely an academic exercise; it is a practical necessity for industries dependent on efficient water and process treatment systems. By understanding their differences, mechanistic roles, and synergistic potential, industries can significantly enhance their operational outcomes while maintaining a commitment to sustainability and regulatory compliance. Such expertise and insight remain vital as the demand for clean water and efficient process systems grows worldwide.

In industrial applications, the selection of specific coagulants and flocculants extends beyond the fundamental chemistry. Considerations include water composition, process economics, regulatory impact, and downstream effects. Industries, from wastewater treatment to mining and food processing, leverage this understanding to improve operational efficiency and regulatory compliance. For instance, a paper mill might select flocculants based on their ability to enhance fiber recovery while minimizing sludge production. Trustworthiness in the choice and application of these chemicals is bolstered by collaborating with reputable suppliers who provide robust technical support and thorough product testing. This ensures the chosen solutions not only meet but exceed industry standards and environmental regulations. This nuanced approach translates into significant economic benefits by reducing chemical consumption, minimizing waste production, and optimizing the overall water or process treatment efficiency. Within industries, adopting tailored solutions tailored to specific water chemistry and operational demands results in reduced operational costs, improved sustainability profiles, and enhanced product quality. Additionally, continual advancements in polymer chemistry and process engineering unlock new potentials for both coagulants and flocculants. Innovations such as biodegradable flocculants or enhanced coagulant formulations with lower toxicity profiles align with the increasing environmental consciousness among industries and consumers alike. In conclusion, distinguishing between flocculants and coagulants is not solely an academic exercise; it is a practical necessity for industries dependent on efficient water and process treatment systems. By understanding their differences, mechanistic roles, and synergistic potential, industries can significantly enhance their operational outcomes while maintaining a commitment to sustainability and regulatory compliance. Such expertise and insight remain vital as the demand for clean water and efficient process systems grows worldwide.
Share
Latest news
-
lk-319-special-scale-and-corrosion-inhibitor-for-steel-plants-advanced-solutions-for-industrial-water-systemsNewsAug.22,2025
-
flocculant-water-treatment-essential-chemical-solutions-for-purification-processesNewsAug.22,2025
-
isothiazolinones-versatile-microbial-control-agents-for-industrial-and-consumer-applicationsNewsAug.22,2025
-
scale-inhibitor-key-solutions-for-water-system-scale-preventionNewsAug.22,2025
-
organophosphonates-versatile-scale-inhibitors-for-industrial-water-systemsNewsAug.22,2025
-
scale-and-corrosion-inhibitor-essential-chemical-solutions-for-water-system-maintenanceNewsAug.22,2025





