cross linked polyacrylamide
Cross-Linked Polyacrylamide Properties, Applications, and Future Trends
Cross-linked polyacrylamide (C-PAM) is a versatile polymer that has garnered significant attention in various fields due to its unique properties and functional characteristics. This article explores the synthesis, properties, applications, and future trends associated with cross-linked polyacrylamide.
Synthesis of Cross-Linked Polyacrylamide
Cross-linked polyacrylamide is synthesized through the polymerization of acrylamide monomers in the presence of a cross-linking agent, such as N,N’-methylenebisacrylamide (MBA). The process typically involves free-radical polymerization, which is initiated using an oxidizing agent or radiation. The degree of cross-linking can be controlled by adjusting the ratio of acrylamide to the cross-linker, yielding a polymer network that exhibits varying degrees of stiffness, solubility, and mechanical strength.
The resulting structure creates a three-dimensional network that entraps solvent molecules, making C-PAM highly effective in various applications, particularly those requiring moisture retention and mechanical stability.
Properties of Cross-Linked Polyacrylamide
Cross-linked polyacrylamide is characterized by several distinct properties
1. Hydrophilicity C-PAM possesses excellent water retention capabilities, making it significantly useful in agricultural and horticultural applications, such as soil conditioning and water conservation.
3. Chemical Stability C-PAM is resistant to a wide range of chemicals, making it suitable for applications in challenging environments where exposure to harsh conditions is inevitable.
4. Biodegradability While polyacrylamide itself is not biodegradable, certain derivatives can be synthesized to enhance environmental compatibility, which is increasingly important in today’s eco-conscious market.
cross linked polyacrylamide
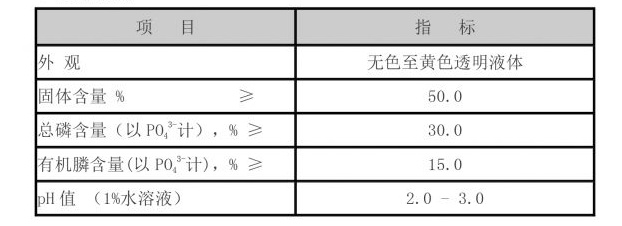
Applications of Cross-Linked Polyacrylamide
Cross-linked polyacrylamide finds utility across diverse sectors
1. Agriculture C-PAM is widely used as a soil conditioner due to its ability to improve soil structure, increase aeration, and enhance water retention, leading to better crop yields. Moreover, it helps in reducing erosion and nutrient leaching.
2. Hydrogels The hydrophilic nature of C-PAM allows for its application in the production of superabsorbent hydrogels, useful in wound dressings, controlled drug delivery systems, and personal care products.
3. Water Treatment C-PAM serves as a flocculant in wastewater treatment processes, where it aids in the removal of suspended particles, enhancing the clarity and quality of water.
4. Cosmetics and Personal Care The polymer’s thickening and binding properties make it a valuable ingredient in various cosmetic formulations, providing desirable textures and stability.
5. Biotechnology C-PAM is increasingly being explored for use in biotechnological applications, including protein purification and all the way to gene therapy techniques, owing to its non-toxic and versatile nature.
Future Trends
Looking ahead, the future of cross-linked polyacrylamide appears promising, driven by ongoing research and technological advancements. Innovations aimed at enhancing its biodegradability and sustainability are at the forefront, with many researchers focusing on developing environmentally friendly alternatives or modifications of C-PAM.
Additionally, the incorporation of C-PAM in smart materials is an emerging trend. Smart hydrogels that respond to external stimuli (pH, temperature, or light) are being explored for applications in drug delivery and tissue engineering.
In conclusion, cross-linked polyacrylamide stands as a critical material in modern science and industry. Its unique properties enable a multitude of applications, from agriculture to advanced biotechnology. As research progresses, it is likely that more environmentally friendly versions of C-PAM will surface, paving the way for sustainable practices while harnessing the functional benefits offered by this remarkable polymer.
-
Understanding Polycarboxylic Acids: Properties, Applications, and Future PotentialNewsJul.28,2025
-
Scale Inhibitor Explained: How to Protect Your System from Limescale and Hard Water DamageNewsJul.28,2025
-
Scale and Corrosion Inhibitors: Essential Chemicals for Industrial Water System ProtectionNewsJul.28,2025
-
Polyaspartic Acid: A Biodegradable Polymer for Sustainable ChemistryNewsJul.28,2025
-
Isothiazolinones: A Versatile Antimicrobial Class with Industrial Power and Regulatory ChallengesNewsJul.28,2025
-
A Deep Dive into 2-Phosphonobutane-1,2,4-Tricarboxylic Acid (PBTC)NewsJul.28,2025





