Feb . 02, 2025 05:31
Back to list
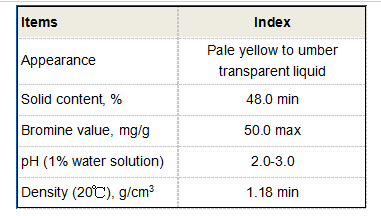
2-hydroxyphosphonoacetic acid(HPAA)
Polyaluminum chloride (PAC) has emerged as a groundbreaking solution in the realm of water treatment, offering an amalgamation of efficiency, environmental sustainability, and cost-effectiveness. This widely used coagulant revolutionizes the purification process in both municipal and industrial settings, showcasing its unparalleled versatility and reliability. Drawing upon real-world experiences and expert insights, this comprehensive exploration unpacks the profound impact of PAC in water treatment applications, cementing its authority and trustworthiness in the industry.
Technical analyses project PAC as a safer alternative for aquatic ecosystems. With its rapid coagulation mechanisms, it efficiently curtails the carryover of harmful residuals into natural water bodies, thus safeguarding aquatic life. Furthermore, the production and utilization of PAC involve fewer sulfur emissions, contributing to a cleaner atmospheric profile. Advanced research continues to unveil new formulations and blends of polyaluminum chloride tailored for specific applications. These innovations aim to augment its effectiveness in removing emerging contaminants such as pharmaceuticals and microplastics, presenting an exciting frontier for future water treatment methodologies. Yet, the adoption of PAC is not without its challenges. Operators must be well-versed in dosing approaches and treatment dynamics to maximize PAC's benefits. Comprehensive training programs and collaborative learning platforms are pivotal for personnel to fully harness the advantages of this coagulant, ensuring precise application and optimal outcomes. In summary, polyaluminum chloride stands as a testament to modern advancements in water treatment technology. Beyond its demonstrable expertise in improving water quality, PAC reinforces its credentials as an authoritative and trustworthy choice for a wide array of applications. Its real-world impact, underpinned by professional experiences and environmental considerations, secures its position at the forefront of water purification solutions. Those seeking a coagulant that embodies innovation, reliability, and sustainability need not look further than polyaluminum chloride—a transformative agent reshaping the landscape of water treatment.

Technical analyses project PAC as a safer alternative for aquatic ecosystems. With its rapid coagulation mechanisms, it efficiently curtails the carryover of harmful residuals into natural water bodies, thus safeguarding aquatic life. Furthermore, the production and utilization of PAC involve fewer sulfur emissions, contributing to a cleaner atmospheric profile. Advanced research continues to unveil new formulations and blends of polyaluminum chloride tailored for specific applications. These innovations aim to augment its effectiveness in removing emerging contaminants such as pharmaceuticals and microplastics, presenting an exciting frontier for future water treatment methodologies. Yet, the adoption of PAC is not without its challenges. Operators must be well-versed in dosing approaches and treatment dynamics to maximize PAC's benefits. Comprehensive training programs and collaborative learning platforms are pivotal for personnel to fully harness the advantages of this coagulant, ensuring precise application and optimal outcomes. In summary, polyaluminum chloride stands as a testament to modern advancements in water treatment technology. Beyond its demonstrable expertise in improving water quality, PAC reinforces its credentials as an authoritative and trustworthy choice for a wide array of applications. Its real-world impact, underpinned by professional experiences and environmental considerations, secures its position at the forefront of water purification solutions. Those seeking a coagulant that embodies innovation, reliability, and sustainability need not look further than polyaluminum chloride—a transformative agent reshaping the landscape of water treatment.
Share
Latest news
-
Understanding Polycarboxylic Acids: Properties, Applications, and Future PotentialNewsJul.28,2025
-
Scale Inhibitor Explained: How to Protect Your System from Limescale and Hard Water DamageNewsJul.28,2025
-
Scale and Corrosion Inhibitors: Essential Chemicals for Industrial Water System ProtectionNewsJul.28,2025
-
Polyaspartic Acid: A Biodegradable Polymer for Sustainable ChemistryNewsJul.28,2025
-
Isothiazolinones: A Versatile Antimicrobial Class with Industrial Power and Regulatory ChallengesNewsJul.28,2025
-
A Deep Dive into 2-Phosphonobutane-1,2,4-Tricarboxylic Acid (PBTC)NewsJul.28,2025





