Exploring the Role of pBTC in Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle and Metabolic Pathways in Organisms
Understanding PBTC and Its Role in the Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle
The tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, also known as the Krebs cycle or citric acid cycle, plays a crucial role in cellular metabolism, specifically in the process of aerobic respiration. It is a series of enzymatic reactions that occur in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells, facilitating the conversion of biochemical energy from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (ATP). One of the key players in this cycle is PBTC (Phenylbutyric Tricarboxylic Acid), a compound that, while not directly part of the cycle, has garnered interest due to its metabolic relevance and potential therapeutic applications.
Structure and Properties of PBTC
PBTC is characterized by its tricarboxylic acid structure, which consists of three carboxylic acid groups attached to a phenylbutyric backbone. This structural configuration endows PBTC with unique properties that allow it to interact with various biological molecules and pathways. The presence of multiple carboxylic acid groups enables it to participate in several biochemical reactions, making it a potentially versatile compound in metabolic regulation.
PBTC in Cellular Metabolism
In the context of the TCA cycle, PBTC does not serve as a direct substrate or intermediate. However, its derivatives and related compounds can have significant effects on metabolic processes. For instance, phenylbutyrate, a well-known derivative of PBTC, has been studied for its ability to modulate energy metabolism, particularly in conditions characterized by metabolic dysregulation such as obesity and insulin resistance.
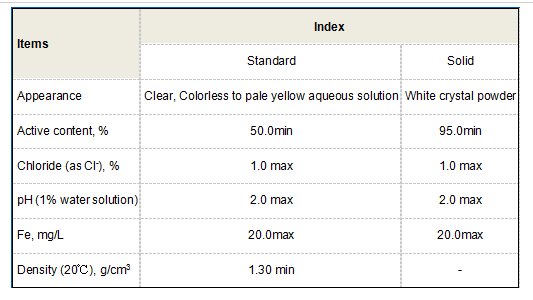
pbtc tricarboxylic acid
Research suggests that PBTC and its derivatives can influence the activity of enzymes within the TCA cycle and other metabolic pathways. By modulating enzyme activity, these compounds may help balance energy production and utilization, which is vital for maintaining cellular health and function. Furthermore, PBTC's potential role in enhancing mitochondrial function is particularly relevant, as mitochondrial health is closely linked to numerous metabolic diseases.
Therapeutic Potential of PBTC
The implications of PBTC in metabolic regulation extend to its potential therapeutic benefits. Studies have indicated that PBTC and similar compounds may possess anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, which could be advantageous in combating chronic diseases often associated with metabolic disturbances. For example, the ability of PBTC to positively affect energy metabolism could have significant implications for conditions such as Type 2 diabetes, where insulin resistance is a key concern.
Moreover, there is ongoing research into the use of PBTC in cancer therapy. Some findings suggest that PBTC can induce apoptosis in cancer cells while sparing healthy cells, making it a candidate for further investigation in targeted cancer treatments. This specificity could provide a valuable strategy in decreasing chemotherapy's side effects while enhancing its efficacy.
Conclusion
In summary, while PBTC may not be a direct component of the tricarboxylic acid cycle, its structural and metabolic properties position it as a significant compound deserving of further study. Its involvement in regulating cellular energy metabolism, coupled with its potential therapeutic applications, highlights the importance of understanding not only traditional metabolic pathways but also the various compounds that influence these pathways. As research continues to evolve, PBTC may emerge as a valuable tool in the field of metabolic medicine, offering new avenues for the treatment of metabolic disorders and related diseases.
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





