polymaleic anhydride
Poly(maleic anhydride) Exploring Its Properties and Applications
Poly(maleic anhydride), often referred to as PMA, is a versatile polymer derived from maleic anhydride. This compound has gained significant attention in various fields due to its unique chemical and physical properties, making it an essential material in industrial and research applications.
Chemical Structure and Properties
PMA is characterized by its alternating double bond structure, a result of the polymerization of maleic anhydride monomers. This structure confers several important properties to PMA, including its solubility in polar solvents and its ability to undergo chemical modifications. The polymer exhibits a high degree of reactivity due to the anhydride functionality, which can easily participate in further reactions, such as hydrolysis, esterification, and amidation, allowing the synthesis of copolymers with varying properties.
One of the remarkable features of PMA is its thermal stability, making it suitable for various applications that require resistance to heat and degradation. Additionally, PMA can form hydrogels, enhancing its utility in biomedical applications, particularly in drug delivery systems where controlled release is crucial.
Applications of Poly(maleic anhydride)
polymaleic anhydride
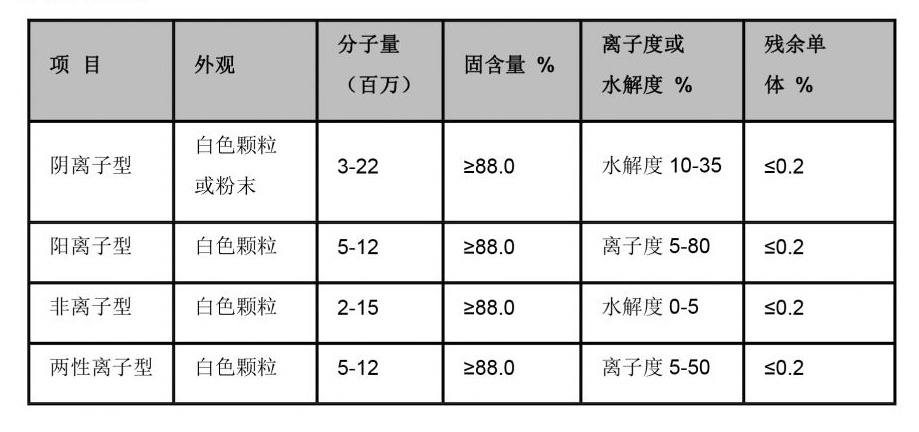
The applications of PMA are diverse, spanning across several industries. In the pharmaceutical sector, PMA’s ability to modify drug release profiles makes it an excellent candidate for drug formulation. It can encapsulate drugs, allowing for sustained release, which is particularly beneficial for chronic conditions requiring long-term medication adherence.
In the field of agriculture, PMA is used in the formulation of dispersants and stabilizers for fertilizers and pesticides, improving their effectiveness and reducing environmental impact. Its biodegradable nature is an added advantage, contributing to more sustainable agricultural practices.
Moreover, PMA finds use in the chemical industry, particularly in the production of additives for plastics and paints. Its efficacy as a thickening agent and dispersing agent enhances the performance of various formulations, thus broadening its commercial applicability.
Conclusion
Poly(maleic anhydride) is a multifunctional polymer with a promising future in numerous fields. Its unique properties, coupled with its ability to be chemically tailored, make it a valuable material in drug delivery, agriculture, and industrial applications. Continued research and development will likely unveil even more innovative uses for PMA, establishing it as a cornerstone in the polymer science landscape. As the demand for sustainable and effective materials grows, poly(maleic anhydride) stands out as a polymer that could meet these challenges head-on.
-
lk-319-special-scale-and-corrosion-inhibitor-for-steel-plants-advanced-solutions-for-industrial-water-systemsNewsAug.22,2025
-
flocculant-water-treatment-essential-chemical-solutions-for-purification-processesNewsAug.22,2025
-
isothiazolinones-versatile-microbial-control-agents-for-industrial-and-consumer-applicationsNewsAug.22,2025
-
scale-inhibitor-key-solutions-for-water-system-scale-preventionNewsAug.22,2025
-
organophosphonates-versatile-scale-inhibitors-for-industrial-water-systemsNewsAug.22,2025
-
scale-and-corrosion-inhibitor-essential-chemical-solutions-for-water-system-maintenanceNewsAug.22,2025





