Հնս . 12, 2024 14:29
Back to list
Cationic PAM is a positively charged polymer.
Understanding Cationic Polyacrylamide (Cationic PAM) A Key Player in Water Treatment and Industrial Applications
Cationic polyacrylamide (Cationic PAM), a synthetic polymer with anionic charge, is a highly versatile substance with a wide range of applications across various industries, particularly in water treatment and waste management. Its chemical structure, characterized by the presence of positively charged amino groups, gives it unique properties that make it indispensable in several processes.
Polyacrylamide (PAM) itself is a linear polymer derived from the polymerization of acrylamide monomers. When functionalized to be cationic, it gains a positive charge, which enables it to interact effectively with negatively charged substances. The percentage of cationic charge, often expressed as cationic%,“ determines its specific application and performance characteristics.
In water treatment, cationic PAM plays a crucial role in flocculation and sedimentation. It acts as a coagulant aid, binding with suspended particles in water to form large flocs that can be easily separated through sedimentation or filtration. The higher the cationic%, the stronger the flocculation ability, making it particularly effective in treating wastewater containing high levels of organic matter or colored substances.
Cationic PAM is also widely used in oil recovery, where it enhances the efficiency of secondary and tertiary recovery methods. The positive charges on the polymer allow it to adhere to the negatively charged rock surfaces in oil reservoirs, improving oil displacement and increasing recovery rates.
In the field of papermaking, cationic PAM is employed as a retention aid. Its positive ions help attract and bind fine fibers and fillers, reducing water content in the paper and improving its quality Its positive ions help attract and bind fine fibers and fillers, reducing water content in the paper and improving its quality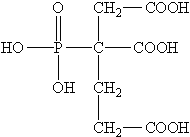 Its positive ions help attract and bind fine fibers and fillers, reducing water content in the paper and improving its quality Its positive ions help attract and bind fine fibers and fillers, reducing water content in the paper and improving its quality
Its positive ions help attract and bind fine fibers and fillers, reducing water content in the paper and improving its quality Its positive ions help attract and bind fine fibers and fillers, reducing water content in the paper and improving its quality cationic pam. The cationic% here is tailored to optimize the interaction between the polymer and the papermaking materials.
Moreover, cationic PAM finds usage in mining,, and agricultural soil conditioning. In mining, it aids in solid-liquid separation, while in textile, it enhances fabric strength and dye uptake. In agriculture, it improves soil structure and water retention, benefiting plant growth.
However, the use of cationic PAM requires careful consideration of factors such as pH, temperature, and the nature of the substances it interacts with. The cationic% must be carefully selected to ensure optimal performance and minimize any potential environmental impacts.
In conclusion, cationic polyacrylamide, with its diverse applications and tunable cationic%, is a vital tool in modern industrial processes. Its effectiveness lies in its ability to manipulate charged interactions, making it an indispensable component in water treatment, oil recovery, papermaking, and more. As technology advances, the potential uses and understanding of cationic PAM are likely to expand further, underlining its importance in the sustainable development of various industries.
cationic pam. The cationic% here is tailored to optimize the interaction between the polymer and the papermaking materials.
Moreover, cationic PAM finds usage in mining,, and agricultural soil conditioning. In mining, it aids in solid-liquid separation, while in textile, it enhances fabric strength and dye uptake. In agriculture, it improves soil structure and water retention, benefiting plant growth.
However, the use of cationic PAM requires careful consideration of factors such as pH, temperature, and the nature of the substances it interacts with. The cationic% must be carefully selected to ensure optimal performance and minimize any potential environmental impacts.
In conclusion, cationic polyacrylamide, with its diverse applications and tunable cationic%, is a vital tool in modern industrial processes. Its effectiveness lies in its ability to manipulate charged interactions, making it an indispensable component in water treatment, oil recovery, papermaking, and more. As technology advances, the potential uses and understanding of cationic PAM are likely to expand further, underlining its importance in the sustainable development of various industries.
 Its positive ions help attract and bind fine fibers and fillers, reducing water content in the paper and improving its quality Its positive ions help attract and bind fine fibers and fillers, reducing water content in the paper and improving its quality
Its positive ions help attract and bind fine fibers and fillers, reducing water content in the paper and improving its quality Its positive ions help attract and bind fine fibers and fillers, reducing water content in the paper and improving its quality cationic pam. The cationic% here is tailored to optimize the interaction between the polymer and the papermaking materials.
Moreover, cationic PAM finds usage in mining,, and agricultural soil conditioning. In mining, it aids in solid-liquid separation, while in textile, it enhances fabric strength and dye uptake. In agriculture, it improves soil structure and water retention, benefiting plant growth.
However, the use of cationic PAM requires careful consideration of factors such as pH, temperature, and the nature of the substances it interacts with. The cationic% must be carefully selected to ensure optimal performance and minimize any potential environmental impacts.
In conclusion, cationic polyacrylamide, with its diverse applications and tunable cationic%, is a vital tool in modern industrial processes. Its effectiveness lies in its ability to manipulate charged interactions, making it an indispensable component in water treatment, oil recovery, papermaking, and more. As technology advances, the potential uses and understanding of cationic PAM are likely to expand further, underlining its importance in the sustainable development of various industries.
cationic pam. The cationic% here is tailored to optimize the interaction between the polymer and the papermaking materials.
Moreover, cationic PAM finds usage in mining,, and agricultural soil conditioning. In mining, it aids in solid-liquid separation, while in textile, it enhances fabric strength and dye uptake. In agriculture, it improves soil structure and water retention, benefiting plant growth.
However, the use of cationic PAM requires careful consideration of factors such as pH, temperature, and the nature of the substances it interacts with. The cationic% must be carefully selected to ensure optimal performance and minimize any potential environmental impacts.
In conclusion, cationic polyacrylamide, with its diverse applications and tunable cationic%, is a vital tool in modern industrial processes. Its effectiveness lies in its ability to manipulate charged interactions, making it an indispensable component in water treatment, oil recovery, papermaking, and more. As technology advances, the potential uses and understanding of cationic PAM are likely to expand further, underlining its importance in the sustainable development of various industries. Share
Latest news
-
Understanding Polycarboxylic Acids: Properties, Applications, and Future PotentialNewsJul.28,2025
-
Scale Inhibitor Explained: How to Protect Your System from Limescale and Hard Water DamageNewsJul.28,2025
-
Scale and Corrosion Inhibitors: Essential Chemicals for Industrial Water System ProtectionNewsJul.28,2025
-
Polyaspartic Acid: A Biodegradable Polymer for Sustainable ChemistryNewsJul.28,2025
-
Isothiazolinones: A Versatile Antimicrobial Class with Industrial Power and Regulatory ChallengesNewsJul.28,2025
-
A Deep Dive into 2-Phosphonobutane-1,2,4-Tricarboxylic Acid (PBTC)NewsJul.28,2025





