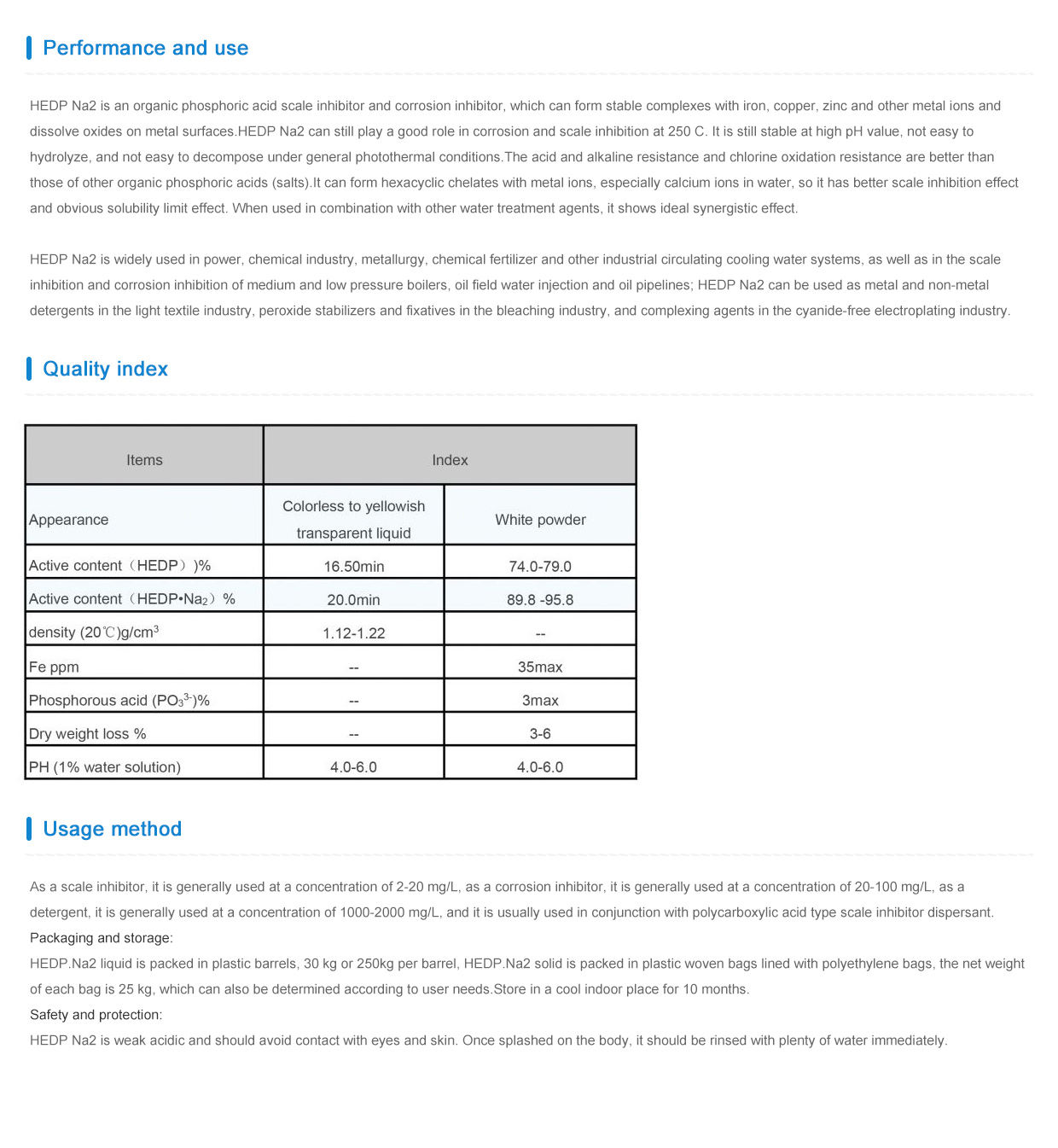
Effective Water Treatment Solutions Using Polyaluminum Chloride for Enhanced Purity and Clarity
The Role of Polyaluminum Chloride in Water Treatment
Water treatment is a critical process that ensures the safety and quality of drinking water and the health of our ecosystems. Among the various coagulants used in water treatment, polyaluminum chloride (PAC) has gained significant attention due to its effectiveness and versatility. This article explores the properties, benefits, and applications of polyaluminum chloride in water treatment processes.
What is Polyaluminum Chloride?
Polyaluminum chloride is a water-soluble polymer that consists of aluminum ions and chloride ions. It appears as a white, powdery substance or a colorless solution, depending on its formulation. PAC is produced by the partial hydrolysis of aluminum chloride, which results in a range of aluminum species with different molecular weights and charge densities. These properties make PAC an effective coagulant for removing turbidity, organic matter, and contaminants from water.
The Water Treatment Process
In water treatment, the coagulation-flocculation process is vital for the removal of suspended particles. When water containing impurities is treated with PAC, the aluminum ions neutralize the negative charges on suspended particles, allowing them to agglomerate and form larger particles called flocs. These flocs can then be easily removed through sedimentation and filtration. This process results in clearer and cleaner water, making it safe for consumption.
Benefits of Using Polyaluminum Chloride
1. High Coagulation Efficiency PAC exhibits superior coagulation performance compared to traditional aluminum sulfate (alum). Its ability to form micro-flocs enhances the rate of sedimentation, which significantly improves the overall efficiency of the treatment process.
polyaluminum chloride water treatment
2. Versatility PAC can be used in various water sources, including surface water, groundwater, and wastewater. Its adaptability allows water treatment facilities to achieve optimal results across different types of water.
3. Lower Dosage Requirements Due to its high charge density, PAC requires lower dosages compared to traditional coagulants. This not only reduces the cost of treatment but also minimizes the production of sludge, leading to easier disposal or further treatment.
4. Wider pH Range PAC is effective over a broader pH range (4.5 to 8.5) than alum, making it suitable for diverse water quality conditions without the need for extensive pH adjustment.
5. Reduced Chemical Residue One of the significant advantages of PAC is that it leaves minimal residual aluminum in treated water compared to alum. This is important for health and regulatory reasons, as high levels of aluminum can pose health risks.
Applications of Polyaluminum Chloride
Polyaluminum chloride is widely used in municipal water treatment plants, industrial wastewater treatment, and even in swimming pool sanitation. In municipal applications, PAC helps ensure that drinking water meets safety standards set by health authorities. In industries, PAC effectively treats wastewater to comply with environmental regulations before discharge. Its use in swimming pools ensures crystal clear water and minimizes the presence of harmful pathogens.
Conclusion
Polyaluminum chloride stands out as a highly effective coagulant in water treatment processes. Its superior coagulation characteristics, lower dosage requirements, and versatility make it an essential component in ensuring water quality. As water treatment technologies evolve, the continued use and development of PAC will play a crucial role in providing safe and clean water for communities and industries around the globe.
-
Understanding Polycarboxylic Acids: Properties, Applications, and Future PotentialNewsJul.28,2025
-
Scale Inhibitor Explained: How to Protect Your System from Limescale and Hard Water DamageNewsJul.28,2025
-
Scale and Corrosion Inhibitors: Essential Chemicals for Industrial Water System ProtectionNewsJul.28,2025
-
Polyaspartic Acid: A Biodegradable Polymer for Sustainable ChemistryNewsJul.28,2025
-
Isothiazolinones: A Versatile Antimicrobial Class with Industrial Power and Regulatory ChallengesNewsJul.28,2025
-
A Deep Dive into 2-Phosphonobutane-1,2,4-Tricarboxylic Acid (PBTC)NewsJul.28,2025





