anionic polyacrylamide uses
Anionic polyacrylamide (APAM) is a versatile polymer widely used in various industries due to its excellent properties. This water-soluble polymer, derived from acrylamide, boasts anionic characteristics, making it particularly useful in applications that require a negative electric charge. Its compound structure allows it to interact effectively with a diverse range of materials, which contributes to its extensive utility across several sectors.
One of the primary applications of anionic polyacrylamide is in water treatment processes. Due to its flocculating properties, APAM is employed to remove suspended particles from water, making it essential in municipal wastewater treatment plants and industrial effluent management. The polymer aggregates suspended particles, facilitating their sedimentation during the filtration process. This not only enhances water clarity but also significantly reduces the levels of harmful contaminants, ensuring that the water meets safety standards before being released back into the environment.
.
Agriculture is another significant field where anionic polyacrylamide has found a multitude of uses. It is applied in soil stabilization and erosion control, promoting better water retention and enhancing soil structure. Farmers utilize APAM to bind soil particles, which helps reduce runoff and soil erosion, particularly in arid regions. Its incorporation into agricultural practices contributes to higher crop yields and better land management. Additionally, APAM is often used in the formulation of superabsorbent materials that can hold substantial amounts of water, thus supporting plant growth in challenging environments.
anionic polyacrylamide uses
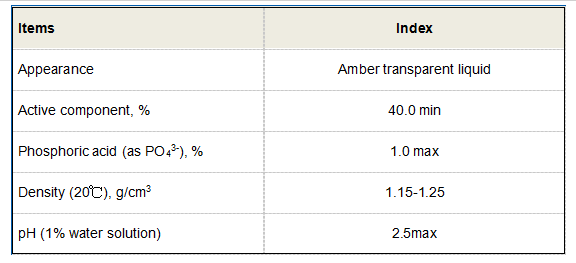
The paper and mining industries also benefit from the use of anionic polyacrylamide. In papermaking, it acts as a retention aid, helping to retain fine particles and improve the quality of the final product. In mining, APAM is utilized in the flotation process, separating valuable minerals from unwanted materials and enhancing the overall efficiency of ore extraction.
As we look toward the future, the demand for anionic polyacrylamide continues to grow, driven by its multifaceted applications across various sectors. However, the environmental impact of its production and use is an important consideration. Research is ongoing to enhance the biodegradability of APAM, ensuring that while it serves vital roles in industry, it does so in an environmentally sustainable manner.
In conclusion, anionic polyacrylamide is an essential polymer with diverse applications spanning water treatment, oil recovery, agriculture, and more. Its unique properties make it a valuable resource in addressing modern challenges across industries, highlighting the importance of ongoing research and innovation in the field.
-
Understanding Polycarboxylic Acids: Properties, Applications, and Future PotentialNewsJul.28,2025
-
Scale Inhibitor Explained: How to Protect Your System from Limescale and Hard Water DamageNewsJul.28,2025
-
Scale and Corrosion Inhibitors: Essential Chemicals for Industrial Water System ProtectionNewsJul.28,2025
-
Polyaspartic Acid: A Biodegradable Polymer for Sustainable ChemistryNewsJul.28,2025
-
Isothiazolinones: A Versatile Antimicrobial Class with Industrial Power and Regulatory ChallengesNewsJul.28,2025
-
A Deep Dive into 2-Phosphonobutane-1,2,4-Tricarboxylic Acid (PBTC)NewsJul.28,2025





