function of poly aluminium chloride in water treatment
The Function of Poly Aluminium Chloride in Water Treatment
Water treatment is an essential process for ensuring the cleanliness and safety of our drinking water and the health of ecosystems. Among the various chemical coagulants used in water treatment, Poly Aluminium Chloride (PAC) has become increasingly popular due to its effectiveness and versatility. This article explores the function of PAC in water treatment processes.
Poly Aluminium Chloride is a polymeric compound that acts as a coagulant for removing suspended solids and impurities from water. When introduced to water, PAC dissolves and dissociates into aluminum ions and polycationic species. The charge neutralization and bridging mechanism are fundamental to its coagulation process. The positive charges of the aluminum ions neutralize the negatively charged particles, such as silt and organic matter, facilitating their aggregation into larger flocs.
One of the primary functions of PAC is to improve the clarity of water by reducing turbidity. Turbidity is often a significant parameter that indicates water quality, and high turbidity levels can negatively affect aquatic life and increase the difficulty of disinfecting water. By using PAC, water treatment facilities can efficiently remove particulate matter, leading to clearer and cleaner water.
In addition to turbidity removal, PAC is effective in the precipitation of dissolved organic matter and color from water sources. Many industrial and agricultural processes introduce organic pollutants into water bodies, leading to discoloration and unpleasant tastes and odors. PAC helps to coagulate these organic materials, allowing them to settle out of the water column during the sedimentation phase of treatment.
function of poly aluminium chloride in water treatment
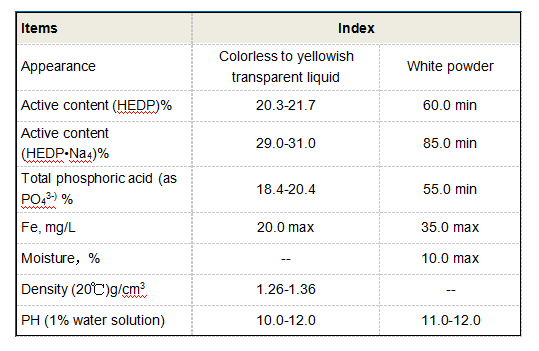
Another important function of PAC is its role in the enhancement of filtration processes. In conventional water treatment systems, PAC helps create larger flocs that are easier to filter. These larger particles can be effectively removed in sedimentation tanks or through sand filters, leaving behind cleaner water for subsequent disinfection processes, such as chlorination or UV treatment.
Moreover, PAC has gained attention due to its lower dosage requirements compared to traditional alum coagulants. This aspect translates to cost savings in chemical usage and reduced production of sludge, which is essential for efficient waste management in water treatment plants. The lower sludge production also lessens the environmental impact of waste disposal, making PAC an eco-friendly choice for many water treatment facilities.
The versatility of PAC also allows for its use in various applications beyond drinking water treatment, including wastewater treatment, paper production, and the treatment of industrial effluents. Its adaptability and efficacy make it a valuable tool in a wide range of water quality management scenarios.
In conclusion, Poly Aluminium Chloride plays a vital function in water treatment by effectively reducing turbidity, removing impurities, enhancing filtration, and offering an eco-friendly alternative to traditional coagulants. As water quality concerns continue to grow globally, the role of PAC will remain critical in ensuring safe and clean water for consumption and environmental preservation. Its ability to meet regulatory standards while being cost-effective positions PAC as a leading choice in modern water treatment practices.
-
The Power of Isothiazolinones in Modern ApplicationsNewsMay.08,2025
-
Flocculants in Water TreatmentNewsMay.08,2025
-
Flocculants and Chemical Solutions: What You Need to KnowNewsMay.08,2025
-
Flocculants and Chemical Solutions: A Growing IndustryNewsMay.08,2025
-
Essential Chemicals: Polymaleic Anhydride and MoreNewsMay.08,2025
-
Acrylic Polymers: Essential Solutions for IndustryNewsMay.08,2025





