jan . 14, 2025 09:43
Back to list
scale inhibitor
Mastering the Use of Scale Inhibitors A Comprehensive Guide to Elevate Your Equipment Longevity
Within the purview of expertise, choosing the appropriate scale inhibitor formulation is paramount. Phosphonates, polycarboxylates, and sulfonates rank among the most recommended classes of inhibitors due to their specific performance profiles. For example, phosphonates exhibit excellent stability over a broad pH range, marking them suitable for systems with variable operational conditions. On the other hand, polycarboxylates are favored for their biodegradable properties, possibly reducing environmental impact. Industry experts advocate conducting compatibility studies to ascertain the best fit for custom scenarios, such as varying water chemistries and system temperatures. Authoritativeness in the application of scale inhibitors is often endorsed by regulatory bodies that set standards to optimize and control their usage. Adhering to these regulations not only ensures safety and efficacy but enhances operational credibility. Trusted guidelines from bodies like the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) and the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) provide frameworks to assist industries in maintaining high standards of environmental and operational health. Building trustworthiness around the use of scale inhibitors is anchored in transparency and ongoing education. Companies that invest in training their personnel on the correct application and handling of these chemicals gain a competitive edge. Seminars, workshops, and certification programs are vital to updating teams about the latest advancements and safety protocols. By prioritizing education, businesses not only foster a culture of competence but demonstrate their commitment to sustainable industrial practices. In conclusion, the selection and application of scale inhibitors should be approached with a comprehensive strategy that combines real-world experience, professional expertise, authoritative guidelines, and a commitment to trust-building. These elements collectively empower industries to harness the full potential of scale inhibitors, optimizing operations and safeguarding the longevity of their equipment—all while supporting a sustainable future in industrial practices.

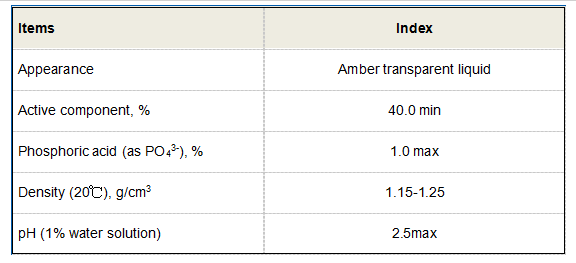
Within the purview of expertise, choosing the appropriate scale inhibitor formulation is paramount. Phosphonates, polycarboxylates, and sulfonates rank among the most recommended classes of inhibitors due to their specific performance profiles. For example, phosphonates exhibit excellent stability over a broad pH range, marking them suitable for systems with variable operational conditions. On the other hand, polycarboxylates are favored for their biodegradable properties, possibly reducing environmental impact. Industry experts advocate conducting compatibility studies to ascertain the best fit for custom scenarios, such as varying water chemistries and system temperatures. Authoritativeness in the application of scale inhibitors is often endorsed by regulatory bodies that set standards to optimize and control their usage. Adhering to these regulations not only ensures safety and efficacy but enhances operational credibility. Trusted guidelines from bodies like the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) and the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) provide frameworks to assist industries in maintaining high standards of environmental and operational health. Building trustworthiness around the use of scale inhibitors is anchored in transparency and ongoing education. Companies that invest in training their personnel on the correct application and handling of these chemicals gain a competitive edge. Seminars, workshops, and certification programs are vital to updating teams about the latest advancements and safety protocols. By prioritizing education, businesses not only foster a culture of competence but demonstrate their commitment to sustainable industrial practices. In conclusion, the selection and application of scale inhibitors should be approached with a comprehensive strategy that combines real-world experience, professional expertise, authoritative guidelines, and a commitment to trust-building. These elements collectively empower industries to harness the full potential of scale inhibitors, optimizing operations and safeguarding the longevity of their equipment—all while supporting a sustainable future in industrial practices.
Share
Next:
Latest news
-
lk-319-special-scale-and-corrosion-inhibitor-for-steel-plants-advanced-solutions-for-industrial-water-systemsNewsAug.22,2025
-
flocculant-water-treatment-essential-chemical-solutions-for-purification-processesNewsAug.22,2025
-
isothiazolinones-versatile-microbial-control-agents-for-industrial-and-consumer-applicationsNewsAug.22,2025
-
scale-inhibitor-key-solutions-for-water-system-scale-preventionNewsAug.22,2025
-
organophosphonates-versatile-scale-inhibitors-for-industrial-water-systemsNewsAug.22,2025
-
scale-and-corrosion-inhibitor-essential-chemical-solutions-for-water-system-maintenanceNewsAug.22,2025





