Hydroxyphosphonoacetic Acid - Properties, Uses, and Applications
Hydroxyphosphonoacetic acid (HPAA) is a phosphonic acid derivative that has garnered attention in various scientific fields, particularly in biochemistry and environmental science. As a compound containing both hydroxy and phosphonic acid groups, HPAA exhibits unique properties that make it a valuable subject for research and application.
One of the most prominent features of hydroxyphosphonoacetic acid is its ability to form stable complexes with metal ions. This characteristic is particularly beneficial in the field of environmental remediation, where heavy metals pose significant threats to ecosystems and human health. Researchers have explored the use of HPAA as a chelating agent to bind and immobilize harmful metal ions, thus preventing their bioavailability and toxicity. The efficacy of HPAA in this context can lead to innovative approaches for treating contaminated water and soil, contributing to sustainable environmental practices.
In addition to its environmental applications, hydroxyphosphonoacetic acid has also been studied for its potential in medicinal chemistry
. Compounds containing phosphonic acid moieties are known for their biological activity, particularly in the inhibition of key enzymes. HPAA, with its unique structure, may exhibit similar inhibitory effects, making it a candidate for further investigation in drug design. Understanding the interactions of HPAA with biological targets could pave the way for the development of new therapeutic agents, particularly in the treatment of diseases where phosphonate compounds have shown promise.hydroxyphosphonoacetic acid
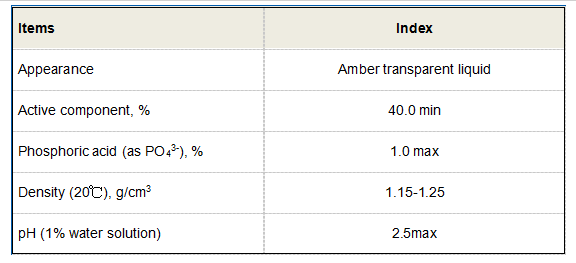
Moreover, the study of HPAA has implications in the agricultural sector. Its properties may be harnessed to enhance the efficiency of fertilizers. As a ligand, HPAA can improve nutrient availability in soil by binding to essential micronutrients and facilitating their uptake by plants. This can lead to optimized plant growth and yield, contributing to food security and sustainable farming practices.
Research on hydroxyphosphonoacetic acid is still in its early stages, but its diverse applications make it a compelling subject for further exploration. Scientists are focused on elucidating its mechanisms of action, its interactions with various biological systems, and its potential uses in environmental clean-up and agriculture. With ongoing studies, HPAA may soon establish itself as a crucial compound in the fields of environmental science, pharmacology, and agri-chemistry, demonstrating the interconnectedness of chemistry and real-world applications.
-
Understanding Polycarboxylic Acids: Properties, Applications, and Future PotentialNewsJul.28,2025
-
Scale Inhibitor Explained: How to Protect Your System from Limescale and Hard Water DamageNewsJul.28,2025
-
Scale and Corrosion Inhibitors: Essential Chemicals for Industrial Water System ProtectionNewsJul.28,2025
-
Polyaspartic Acid: A Biodegradable Polymer for Sustainable ChemistryNewsJul.28,2025
-
Isothiazolinones: A Versatile Antimicrobial Class with Industrial Power and Regulatory ChallengesNewsJul.28,2025
-
A Deep Dive into 2-Phosphonobutane-1,2,4-Tricarboxylic Acid (PBTC)NewsJul.28,2025





