Feb . 14, 2025 03:26
Back to list
polyaluminum chloride water treatment
Poly aluminium chloride (PAC), a coagulant widely utilized in wastewater treatment, has transformed purification processes with its efficiency and reliability. Derived from aluminium salts, PAC has gained prominence due to its ability to produce larger flocs compared to traditional coagulants like aluminum sulfate. This characteristic enhances sedimentation and filtration, therefore leading to clearer water.
In terms of authoritativeness, numerous studies corroborate PAC's efficacy in suspended solid and colloidal particle removal. Peer-reviewed research consistently illustrates PAC's ability to outperform other coagulants in removing turbidity and dissolved organic matter, crucial for achieving regulatory compliance and reducing ecological impacts. The alignment of empirical evidence with practical application offers a solid foundation, positioning PAC as a dependable option in the realm of industrial water cleanup. Trustworthiness surrounds not only PAC’s environmental benefits but also its economic merits. Facilities have observed measurable cost savings by reducing other chemical inputs and improving overall process efficiency. Additionally, PAC’s stable pricing, due to its widespread manufacturing and availability, enables facilities to plan budgets with accuracy, avoiding fluctuations that complicate financial management. Moreover, using PAC aligns with sustainable environmental practices. Its role in decreasing sludge volume minimizes waste generation and disposal needs. This sustainable aspect appeals to environmentally conscious organizations aiming to achieve corporate social responsibility targets and enhance their green credentials. Conclusively, poly aluminium chloride stands as a cornerstone in advanced water treatment practices. Its consistent results, ease of use, and cost-effectiveness affirm its place within modern purification systems. As industries push towards sustainable and efficient operations, PAC offers a symbiotic balance of meeting regulatory standards and optimizing operational efficiencies. Through continual advancements in PAC formulations, its application is poised to adapt to future challenges, reinforcing its role as an indispensable component in water treatment arsenals worldwide.

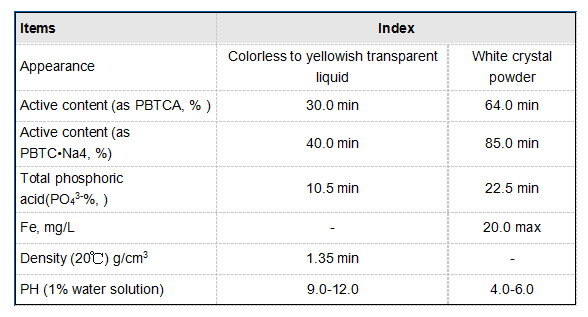
In terms of authoritativeness, numerous studies corroborate PAC's efficacy in suspended solid and colloidal particle removal. Peer-reviewed research consistently illustrates PAC's ability to outperform other coagulants in removing turbidity and dissolved organic matter, crucial for achieving regulatory compliance and reducing ecological impacts. The alignment of empirical evidence with practical application offers a solid foundation, positioning PAC as a dependable option in the realm of industrial water cleanup. Trustworthiness surrounds not only PAC’s environmental benefits but also its economic merits. Facilities have observed measurable cost savings by reducing other chemical inputs and improving overall process efficiency. Additionally, PAC’s stable pricing, due to its widespread manufacturing and availability, enables facilities to plan budgets with accuracy, avoiding fluctuations that complicate financial management. Moreover, using PAC aligns with sustainable environmental practices. Its role in decreasing sludge volume minimizes waste generation and disposal needs. This sustainable aspect appeals to environmentally conscious organizations aiming to achieve corporate social responsibility targets and enhance their green credentials. Conclusively, poly aluminium chloride stands as a cornerstone in advanced water treatment practices. Its consistent results, ease of use, and cost-effectiveness affirm its place within modern purification systems. As industries push towards sustainable and efficient operations, PAC offers a symbiotic balance of meeting regulatory standards and optimizing operational efficiencies. Through continual advancements in PAC formulations, its application is poised to adapt to future challenges, reinforcing its role as an indispensable component in water treatment arsenals worldwide.
Share
Next:
Latest news
-
Pbtc Scale InhibitorPBTC: A Scale Protector for Industrial Water TreatmentNewsAug.05,2025
-
Organic Phosphonate: An Efficient Defender in the Field of Scale InhibitionNewsAug.05,2025
-
Hydrolyzed Polymaleic Anhydride: Green Pioneer in Scale Inhibition FieldNewsAug.05,2025
-
PAPEMP Polyamino Polyether Methylene Phosphonic Acid For SaleNewsAug.05,2025
-
Flocculant Water Treatment: A Pioneer in Purification in the Field of Water TreatmentNewsAug.05,2025
-
Benzyl Isothiazolinone: An Efficient and Broad-Spectrum Antibacterial Protective GuardNewsAug.05,2025





