6月 . 27, 2024 08:14
Back to list
Exploring Polyacrylamide Functionality in Biomedical Applications
The Functional Versatility of Polyacrylamide
Polyacrylamide, a synthetic polymer, is renowned for its multifunctional nature that transcends various scientific and industrial applications. This versatile compound is formed by the polymerization of acrylamide monomers, creating a long-chain polymer with remarkable physical and chemical properties. Its ability to function as a flocculant, thickener, or gel, depending on its molecular weight and degree of cross-linking, makes it an invaluable material across diverse fields.
In the realm of biochemistry, polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) is pivotal for separating proteins based on their size. The porous structure of the gel matrix allows smaller molecules to move faster than larger ones under an applied electric field, enabling researchers to analyze protein samples effectively. Additionally, polyacrylamide's hydrophilic nature ensures minimal interaction with the proteins, preserving their native conformation and activity.
The structural robustness of polyacrylamide is exploited in civil engineering, where it serves as a soil stabilization agent. By mixing polyacrylamide powder with soil, engineers can improve the soil's load-bearing capacity and reduce dust formation. This application not only enhances construction efficiency but also minimizes environmental impact by reducing the need for new materials.
Polyacrylamides are also essential in water treatment processes. Their exceptional flocculation properties help in the removal of suspended particles from water by forming bridges between particles, causing them to aggregate and settle Their exceptional flocculation properties help in the removal of suspended particles from water by forming bridges between particles, causing them to aggregate and settle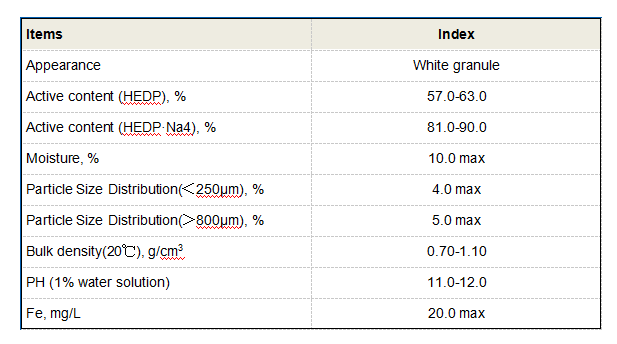 Their exceptional flocculation properties help in the removal of suspended particles from water by forming bridges between particles, causing them to aggregate and settle Their exceptional flocculation properties help in the removal of suspended particles from water by forming bridges between particles, causing them to aggregate and settle
Their exceptional flocculation properties help in the removal of suspended particles from water by forming bridges between particles, causing them to aggregate and settle Their exceptional flocculation properties help in the removal of suspended particles from water by forming bridges between particles, causing them to aggregate and settle polyacrylamide function. This process significantly improves water clarity and quality, making it suitable for consumption and other uses.
In the textile industry, polyacrylamide is used as a soil release agent. It reduces the adhesion of dirt to fabric fibers, making laundry cleaning more effective and extending the lifespan of clothing. Furthermore, the polymer acts as a lubricant in spinning yarns, improving the strength and uniformity of the final product.
Medical applications of polyacrylamide have also emerged, such as its use in contact lens materials due to its excellent oxygen permeability and comfort for the eye. Moreover, polyacrylamide-based hydrogels show promise in drug delivery systems because they can encapsulate drugs and release them in a controlled manner, enhancing therapeutic efficacy while minimizing side effects.
In summary, the functional versatility of polyacrylamide is evident through its broad spectrum of applications ranging from scientific research to industrial processes and beyond. Its unique properties make it an indispensable component in numerous products and procedures, underscoring its importance in modern technological advancements. As innovation continues, the potential uses for this adaptable polymer will undoubtedly expand, further cementing its status as a cornerstone material in science and industry.
polyacrylamide function. This process significantly improves water clarity and quality, making it suitable for consumption and other uses.
In the textile industry, polyacrylamide is used as a soil release agent. It reduces the adhesion of dirt to fabric fibers, making laundry cleaning more effective and extending the lifespan of clothing. Furthermore, the polymer acts as a lubricant in spinning yarns, improving the strength and uniformity of the final product.
Medical applications of polyacrylamide have also emerged, such as its use in contact lens materials due to its excellent oxygen permeability and comfort for the eye. Moreover, polyacrylamide-based hydrogels show promise in drug delivery systems because they can encapsulate drugs and release them in a controlled manner, enhancing therapeutic efficacy while minimizing side effects.
In summary, the functional versatility of polyacrylamide is evident through its broad spectrum of applications ranging from scientific research to industrial processes and beyond. Its unique properties make it an indispensable component in numerous products and procedures, underscoring its importance in modern technological advancements. As innovation continues, the potential uses for this adaptable polymer will undoubtedly expand, further cementing its status as a cornerstone material in science and industry.
 Their exceptional flocculation properties help in the removal of suspended particles from water by forming bridges between particles, causing them to aggregate and settle Their exceptional flocculation properties help in the removal of suspended particles from water by forming bridges between particles, causing them to aggregate and settle
Their exceptional flocculation properties help in the removal of suspended particles from water by forming bridges between particles, causing them to aggregate and settle Their exceptional flocculation properties help in the removal of suspended particles from water by forming bridges between particles, causing them to aggregate and settle polyacrylamide function. This process significantly improves water clarity and quality, making it suitable for consumption and other uses.
In the textile industry, polyacrylamide is used as a soil release agent. It reduces the adhesion of dirt to fabric fibers, making laundry cleaning more effective and extending the lifespan of clothing. Furthermore, the polymer acts as a lubricant in spinning yarns, improving the strength and uniformity of the final product.
Medical applications of polyacrylamide have also emerged, such as its use in contact lens materials due to its excellent oxygen permeability and comfort for the eye. Moreover, polyacrylamide-based hydrogels show promise in drug delivery systems because they can encapsulate drugs and release them in a controlled manner, enhancing therapeutic efficacy while minimizing side effects.
In summary, the functional versatility of polyacrylamide is evident through its broad spectrum of applications ranging from scientific research to industrial processes and beyond. Its unique properties make it an indispensable component in numerous products and procedures, underscoring its importance in modern technological advancements. As innovation continues, the potential uses for this adaptable polymer will undoubtedly expand, further cementing its status as a cornerstone material in science and industry.
polyacrylamide function. This process significantly improves water clarity and quality, making it suitable for consumption and other uses.
In the textile industry, polyacrylamide is used as a soil release agent. It reduces the adhesion of dirt to fabric fibers, making laundry cleaning more effective and extending the lifespan of clothing. Furthermore, the polymer acts as a lubricant in spinning yarns, improving the strength and uniformity of the final product.
Medical applications of polyacrylamide have also emerged, such as its use in contact lens materials due to its excellent oxygen permeability and comfort for the eye. Moreover, polyacrylamide-based hydrogels show promise in drug delivery systems because they can encapsulate drugs and release them in a controlled manner, enhancing therapeutic efficacy while minimizing side effects.
In summary, the functional versatility of polyacrylamide is evident through its broad spectrum of applications ranging from scientific research to industrial processes and beyond. Its unique properties make it an indispensable component in numerous products and procedures, underscoring its importance in modern technological advancements. As innovation continues, the potential uses for this adaptable polymer will undoubtedly expand, further cementing its status as a cornerstone material in science and industry. Share
Latest news
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





