coagulant and flocculant chemicals
The Role of Coagulant and Flocculant Chemicals in Water Treatment
Water treatment is a critical process aimed at ensuring the safety and purity of drinking water and protecting aquatic ecosystems. Two essential classes of chemicals that play a pivotal role in this process are coagulants and flocculants. Though often used interchangeably, these substances serve distinct functions in the clarification of water.
Coagulants are chemicals that help remove suspended particles from water by neutralizing their charges. Most particles present in water, such as mud, silt, and organic matter, carry a negative charge. This charge repels similar particles, preventing them from clumping together and settling at the bottom. Coagulants, such as aluminum sulfate (alum) and ferric chloride, are positively charged and can neutralize the charges of these particles. Once the charge is neutralized, the particles can begin to agglomerate into larger clusters known as 'flocs.'
The process initiated by coagulants is known as coagulation. During this phase, the addition of coagulants leads to the formation of small, floc-like structures. However, coagulation alone does not sufficiently clarify water; it must be followed by another essential stage—flocculation.
Flocculants are substances that facilitate the aggregation of these small flocs into larger, more settleable formations. These chemicals are often long-chain polymers that promote the bridging of smaller particles, allowing for the formation of larger flocs that can be more easily removed from the water. Common flocculants include polyacrylamides and synthetic organic polymers.
coagulant and flocculant chemicals
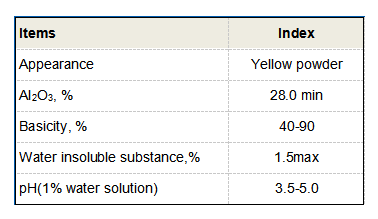
The combination of coagulants and flocculants is crucial for effective water treatment. The coagulant first destabilizes the particles, while the flocculant enhances the formation of larger aggregates. This dual action results in increased efficiency in removing impurities from water. Once adequately sized, flocs can be removed through sedimentation or filtration, significantly reducing turbidity and improving water quality.
The selection of appropriate coagulant and flocculant chemicals depends on various factors, including the characteristics of the water source, the nature of the contaminants, and regulatory requirements. Different applications may call for different products; for example, drinking water treatment may necessitate specific standards for chemical use compared to wastewater treatment.
In recent years, environmental considerations have prompted a shift towards more sustainable practices in the use of coagulant and flocculant chemicals. Innovations in biodegradable polymers and natural coagulants sourced from plants are paving the way for greener alternatives in the water treatment industry. Furthermore, ongoing research seeks to enhance the effectiveness of these chemicals while minimizing potential ecological impacts.
In conclusion, the combined use of coagulant and flocculant chemicals is integral to the water treatment process. They not only improve water clarity but also contribute to public health and environmental conservation. As the industry advances towards more sustainable practices, the importance of these chemicals will likely continue to evolve, underscoring their role in ensuring safe, clean, and environmentally friendly water treatment solutions.
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





