Zinc HEDP Applications and Benefits for Water Treatment Solutions
Understanding Zinc HEDP A Comprehensive Overview
Zinc HEDP, which stands for Zinc Hydroxyethylidene Diphosphonic Acid, is a chemical compound that has gained significant attention in various industries due to its unique properties and applications. As a derivative of HEDP (Hydroxyethylidene Diphosphonic Acid), it combines the benefits of zinc ions with the efficacy of phosphonate chemistry, making it a valuable agent in water treatment, corrosion inhibition, and other fields.
Composition and Chemistry of Zinc HEDP
Zinc HEDP is a chelating agent formed by the reaction of zinc salts with HEDP. The resulting compound exhibits a strong affinity for metal ions, which not only enhances its stability but also increases its effectiveness in various applications. With its dual function as a zinc source and a corrosion inhibitor, Zinc HEDP is particularly relevant in industries dealing with water systems, oil and gas production, and even in agriculture.
The chemical structure of Zinc HEDP allows it to bind effectively with calcium and other metal ions, which is crucial in preventing scale formation in water systems. The phosphonate groups in the compound help in disrupting the crystallization of calcium carbonate, thereby maintaining the efficiency of water systems and boilers.
Applications of Zinc HEDP
.
2. Corrosion Inhibition Zinc HEDP serves as an effective corrosion inhibitor for various metal surfaces. It forms a protective film on metal surfaces, thereby shielding them from aggressive environmental factors such as moisture and oxygen that typically contribute to corrosion processes. This property is particularly advantageous in industries such as automotive, construction, and manufacturing, where metal integrity is crucial.
'zn hedp 锌hedp'
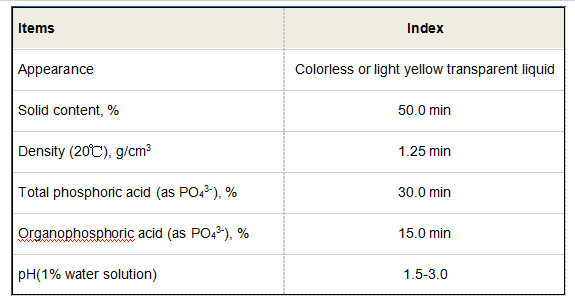
3. Agriculture In agriculture, Zinc HEDP has potential applications as a micronutrient fertilizer. Zinc is an essential trace element for plant growth, and its availability in a chelated form helps in improving its uptake by plants. This can lead to enhanced growth and yield in crops that are deficient in zinc.
4. Oil and Gas Industry The oil and gas industry benefits from Zinc HEDP in terms of its usage in drilling fluids and enhanced oil recovery processes. The compound helps in controlling scale formation and improving the overall productivity of oil extraction processes. It plays a vital role in maintaining the efficiency of operations in harsh environments.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Zinc HEDP exhibits low toxicity levels, making it a safer alternative to many traditional chemicals used in water treatment and industrial applications. However, like all chemical substances, it should be handled with care and according to safety guidelines to minimize any potential risks to human health and the environment.
The use of Zinc HEDP also aligns with the growing trend toward sustainable practices in industrial processes. As industries seek to reduce their environmental footprint, the integration of less harmful and more efficient chemicals becomes increasingly important. Zinc HEDP, with its multifunctional properties, supports these efforts by providing effective solutions while adhering to safety and environmental standards.
Conclusion
Zinc HEDP is a remarkable chemical compound that offers various benefits across multiple industries. Its combination of zinc's effectiveness in preventing corrosion and HEDP's scale inhibition properties makes it an invaluable resource in water treatment, agriculture, and industrial applications. As industries continue to seek efficient and environmentally friendly solutions, the demand for compounds like Zinc HEDP is likely to grow. Understanding its properties and applications can pave the way for innovations that enhance productivity while maintaining safety and environmental integrity. Whether in managing industrial water systems or enhancing agricultural practices, Zinc HEDP stands out as a versatile and effective solution in the modern industrial landscape.
-
Pbtc Scale InhibitorPBTC: A Scale Protector for Industrial Water TreatmentNewsAug.05,2025
-
Organic Phosphonate: An Efficient Defender in the Field of Scale InhibitionNewsAug.05,2025
-
Hydrolyzed Polymaleic Anhydride: Green Pioneer in Scale Inhibition FieldNewsAug.05,2025
-
PAPEMP Polyamino Polyether Methylene Phosphonic Acid For SaleNewsAug.05,2025
-
Flocculant Water Treatment: A Pioneer in Purification in the Field of Water TreatmentNewsAug.05,2025
-
Benzyl Isothiazolinone: An Efficient and Broad-Spectrum Antibacterial Protective GuardNewsAug.05,2025





