Effective Solutions for Water Treatment Using PAM Technology and Techniques
Understanding PAM Water Treatment An Innovative Approach to Water Purification
Water has become one of the most precious resources on our planet, necessitating its effective treatment to ensure safety and sustainability. One of the promising methods in water treatment involves the use of Polyacrylamide (PAM), a synthetic polymer that has garnered attention for its effectiveness in various applications. This article discusses PAM’s role in water treatment processes, its benefits, and its environmental considerations.
What is Polyacrylamide (PAM)?
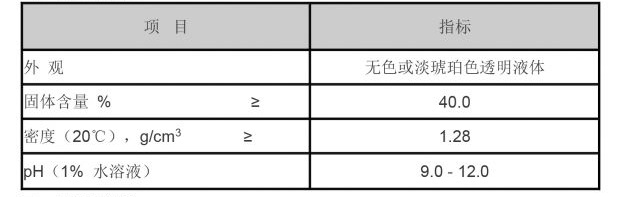
Polyacrylamide is a water-soluble polymer that is derived from the polymerization of acrylamide monomers. It is known for its ability to flocculate, which means it can bind small particles together to form larger aggregates or flocs. These flocs can then be more easily removed from water, making PAM invaluable in water treatment applications. PAM can exist in various forms, including anionic, cationic, and nonionic variants, each suited for specific treatment scenarios.
Applications of PAM in Water Treatment
PAM is primarily used in two main areas of water treatment municipal wastewater treatment and industrial water management.
1. Municipal Wastewater Treatment In municipal applications, PAM is often used to enhance the sedimentation processes in wastewater treatment plants. It acts as a flocculant, helping to clump suspended solids, organic matter, and other impurities, making it easier to remove them through sedimentation or filtration. This results in cleaner effluent being discharged into water bodies, thus protecting aquatic ecosystems.
2. Industrial Water Management Industries that generate significant amounts of wastewater, such as mining, paper manufacturing, and oil production, utilize PAM to manage their water treatment needs. In such contexts, PAM helps to stabilize slurries, reducing the amount of wastewater that needs treatment and facilitating the recovery of valuable resources.
Benefits of Using PAM
pam water treatment
The use of PAM in water treatment comes with numerous benefits
- Efficiency in Removal of Contaminants PAM increases the efficiency of removing suspended solids and contaminants from water. This leads to better clarification, allowing for higher-quality treated water.
- Cost-Effectiveness While PAM is a synthetic product, its effective operation reduces the overall resource and time required for water treatment processes, thereby lowering operational costs for treatment facilities.
- Improved Water Quality The use of PAM enhances the overall quality of the treated water, ensuring it meets regulatory standards and is safe for discharge into the environment or for reuse applications.
- Versatility The different forms of PAM allow it to be tailored for various water treatment applications, making it a flexible solution for both municipal and industrial water management challenges.
Environmental Considerations
Despite its advantages, the use of PAM warrants careful consideration of its environmental impact. One concern is the potential toxicity of residual acrylamide, particularly in the cationic forms of PAM, which can be harmful to aquatic life if not mitigated. Therefore, it is crucial to monitor and manage the concentration of PAM in treated effluents to comply with environmental regulations.
Conclusion
PAM water treatment presents an innovative and effective approach to managing water purification challenges. Its ability to enhance flocculation makes it a valuable tool for both municipal and industrial applications. However, like all chemical agents, it is essential to use PAM responsibly, ensuring that its benefits are realized without compromising environmental integrity. As water scarcity and pollution remain pressing global issues, PAM stands out as a powerful solution in the quest for cleaner and safer water resources.
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





