flocculation chemicals
Understanding Flocculation Chemicals Key to Efficient Water Treatment
Flocculation is a crucial process in water treatment, playing a significant role in the removal of suspended particles, colloids, and impurities from water. The effectiveness of flocculation largely depends on the choice and application of flocculation chemicals. These chemicals, when added to wastewater or drinking water, facilitate the agglomeration of tiny particles into larger flocs, which can then be removed through sedimentation or filtration. In this article, we will explore the types of flocculation chemicals, their functions, and their significance in water treatment processes.
Types of Flocculation Chemicals
Flocculation chemicals can be categorized into several groups, primarily based on their chemical composition and mechanisms of action. The most common types include
1. Coagulants These chemicals neutralize the electric charges on suspended particles, allowing them to clump together. Common coagulants include aluminum sulfate (alum), ferric chloride, and polymers like polyaluminum chloride. They are pivotal in the initial phase of flocculation, altering the properties of the particles to promote aggregation.
2. Flocculants Once the particles have been coagulated, flocculants come into play. These are typically high-molecular-weight organic compounds, such as polyacrylamides, that enhance the formation of larger aggregates (flocs) by providing a bridge between the particles. Flocculants improve the settling rates of flocs and increase the efficiency of the filtration process.
3. pH Adjusters Sometimes, adjusting the pH of the water is necessary to optimize the performance of coagulants and flocculants. Common pH adjusters include lime (calcium hydroxide) and sulfuric acid. Maintaining the correct pH is essential to ensure maximum effectiveness in particle removal.
flocculation chemicals
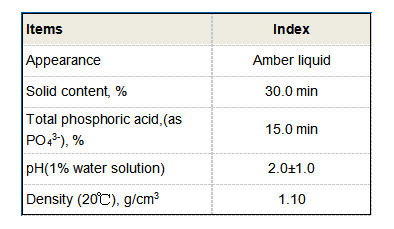
Importance of Flocculation Chemicals in Water Treatment
The application of flocculation chemicals is vital for several reasons. Firstly, they significantly improve the clarity of water by reducing turbidity, making it safe for drinking and other uses. In industrial processes, flocculation chemicals help in the effective recycling of water, leading to reduced operational costs and environmental impact.
Secondly, flocculation plays a key role in the treatment of municipal wastewater. By effectively removing solids and pollutants from wastewater, flocculation chemicals contribute to protecting aquatic ecosystems and enhancing the quality of treated water discharged into rivers and oceans.
Additionally, the use of flocculation chemicals can lead to improved sludge management. Efficient flocculation increases the density of the sludge, making it easier to dewater and manage, ultimately leading to reduced disposal costs and environmental benefits.
Conclusion
Flocculation chemicals are indispensable in modern water treatment processes. Their ability to promote the aggregation of suspended particles ensures the effective removal of impurities, contributing to cleaner water and better environmental outcomes. As water quality regulations become more stringent, the innovative application of flocculation chemicals will continue to evolve, providing essential solutions for sustainable water management. Understanding the types and functions of these chemicals is fundamental for anyone involved in water treatment, ensuring that we can maintain the quality of this precious resource for future generations.
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





